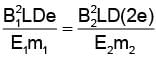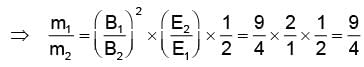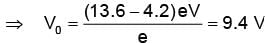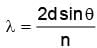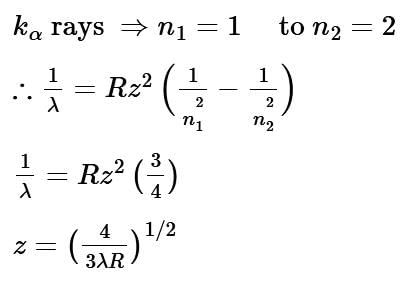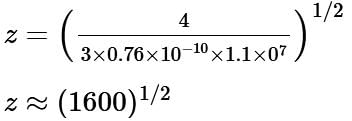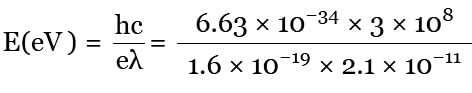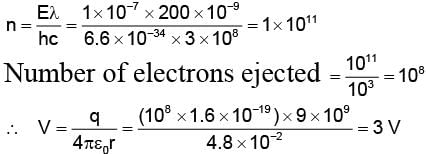Test: Dual Nature of Matter - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 12 - Test: Dual Nature of Matter
What is the de-Broglie wavelength associated with an electron accelerated through a potential of 100 volts?
An α – particle and a deutron are accelerated through the same potential difference. What will be the ratio of their de-Broglie wavelength?
The work function of metal is 1 eV. Light of wavelength 3000 Å is incident on this metal surface. The velocity of emitted photo-electrons will be
Of the following moving with the same momentum, the one which has the largest wavelength is
The work function of a metallic surface is 5.01 eV. The photo-electrons are emitted when light of wavelength 2000 Å falls on it. The potential difference applied to stop the fastest photo-electrons is [ h = 4.14 x 10-15 eV sec]
A particle of mass M at rest decays into two particles of masses m1 and m2, having non-zero velocities. The ratio of the de-Broglie wavelengths of the particles, l1/l2 is
When photon of energy 4.25 eV strike the surface of a metal A, the ejected photoelectrons have maximum kinetic energy TA eV and de-Broglie wavelength λA. The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons liberated from another metal B by photon of energy 4.70 eV is TB = (TA - 1.50) eV. If the de-Broglie wavelength of these photoelectrons is lB = 2lA, then
The de-Broglie wavelength of an electron is 1.0 nm. What is the retarding potential required to stop it?
In a photoemissive cell with executing wavelength λ, the fastest electron has speed v. If the exciting wavelength is changed to 3λ/4, the speed of the fastest emitted electron will be
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequencies v1 and v2 of the incident light rays (v1 > v2). If the maximum values of kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the two cases are in the ratio of 1 : k, then the threshold frequency of the metallic surface is
An X-ray tube is operating at 50 kV and 20 mA. The target material of the tube has a mass of 1.0 kg and specific heat 495 J kg–1°C–1. One percent of the supplied electric power is converted into X-rays and the entire remaining energy goes into heating the target. Then
Electrons with energy 80 keV are incident on the tungsten target of an X-ray tube. K shell electrons of tungsten have ionization energy 72.5 keV. X-rays emitted by the tube contain only
The X-ray wavelength of Lα line of platinum (Z = 78) is 1.30 Å. The X-ray wavelength of Lα line of Molybdenum (Z = 42) is
The ratio of de-Broglie wavelengths of molecules of hydrogen and helium which are at temperature 27°C and 127°C respectively is
A photon of wavelength 6630 Å is incident on a totally reflecting surface. The momentum delivered by the photon is equal to
The ratio of de-Broglie wavelength of α-particle to that of a proton being subjected to the same magnetic field so that the radii of their path are equal to each other assuming the field induction vector 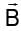 is perpendicular to the velocity vectors of the α-particle and the proton is
is perpendicular to the velocity vectors of the α-particle and the proton is
The potential energy of a particle of mass m is given by 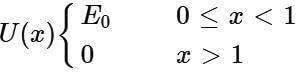 λ1 and λ2 are the de-Broglie wavelength of the particle, when 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 and x > 1 respectively. If the total energy of particle is 2E0, then the ratio λ1/λ2 will be
λ1 and λ2 are the de-Broglie wavelength of the particle, when 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 and x > 1 respectively. If the total energy of particle is 2E0, then the ratio λ1/λ2 will be
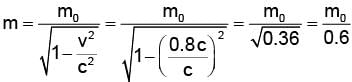
Rest mass energy of an electron is 0.51 MeV. If this electron is moving with a velocity 0.8 c (where c is velocity of light in vacuum), then kinetic energy of the electrostatic should be
A proton, a deuteron and an a-particle having the same momentum, enters a region of uniform electric field between the parallel plates of a capacitor. The electric field is perpendicular to the initial path of the particles. Then the ratio of deflections suffered by them is
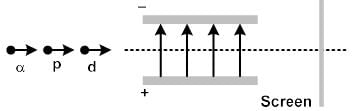
In order to coincide the parabolas formed by singly ionized ions in one spectrograph and doubly ionized ions in the other Thomson's mass spectrograph, the electric fields and magnetic fields are kept in the ratios 1: 2 and 3: 2 respectively. Then the ratio of masses of the ions is
Light from a hydrogen discharge tube is incident on the cathode of a photoelectric cell the work function of the cathode surface is 4.2 eV. In order to reduce the photocurrent to zero the voltage of the anode relative to the cathode must be made
The largest distance between the interatomic planes of a crystal is 10–7 cm. The upper limit for the wavelength of Xrays which can be usefully studied with this crystal is
The wavelength of Kα X-rays produced by an X-ray tube is 0.76 Å. The atomic number of the anode material of the tube is
The Kα X-ray emission line of tungsten occurs at λ = 0.021 nm. The energy difference between K and L levels in this atom is about
A silver ball of radius 4.8 cm is suspended by a thread in the vacuum chamber. UV light of wavelength 200 nm is incident on the ball for some times during which a total energy of 1 × 10–7 J falls on the surface. Assuming on an average one out of 103 photons incident is able to eject electron. The potential on sphere will be
|
88 videos|421 docs|88 tests
|



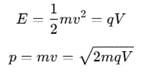
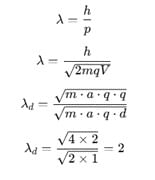

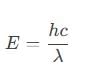
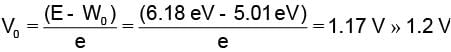
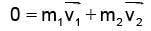
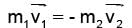
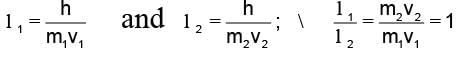


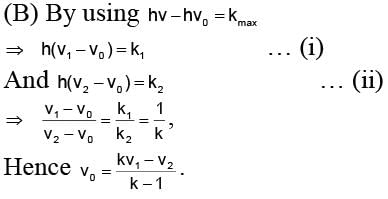
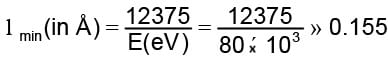
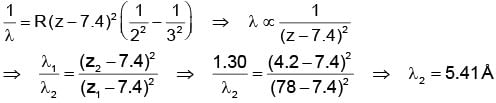
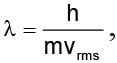 rms velocity of a gas particle at the given temperature (T) is given as
rms velocity of a gas particle at the given temperature (T) is given as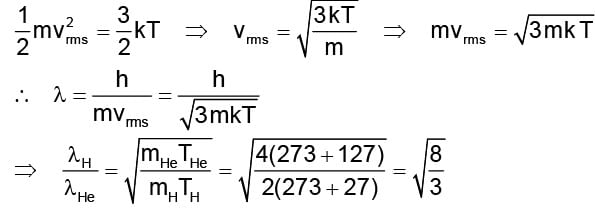
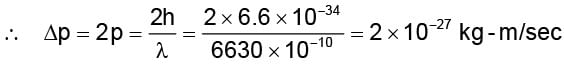
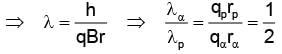


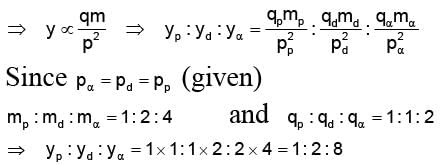
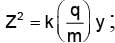 where
where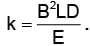 For parabolas to coincide in the two photographs, the kq/m, should be same for the two cases. Thus,
For parabolas to coincide in the two photographs, the kq/m, should be same for the two cases. Thus,