Practice Test - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test 4 Months Preparation for NEET - Practice Test
The electromagnetic waves ranging in frequencies between 1 GHz and 300 GHz are called _______
Plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction. If the frequency of the wave is 30 MHz, its wavelength is
Referring to the Young’s double slit experiment, Phase difference corresponding to a Path Difference of λ /3 is
The angle of incidence at which the reflected beam is fully polarized is called
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-21) This section contains 21 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q. For zeroth order reaction,
A → B
[A]0 = 0.01 M, [A]t = 0.008Matter 10 min.
Thus, half-life is
A Certain Zeroth Order reaction has k = 0.025 Ms-1 for the disappearance of A. What will be the concentration of A after 15s, if the intial concentration is 0.50 M?
For Zeroth Order Reaction, variation of x with time is shown as
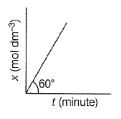
Q. At initial concenration of the reactant as 17.32 min dm-1 , half - life period is
In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant decreases from 0.8 M to 0.4 M is 15 min. The time taken for the concentration to change from 0.1 M to 0.025 M is
For the First order reaction, concentration of the reactant after two averagelives is reduced to
For the first order reaction,
A → Product
Q. The concentration of A changes from 0.1 M to 0.025 M in 40 min. The rate of the reaction when the concentration of A is 0.01 M is
[AIEEE 2012]
For the reaction,
A → Products, 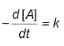
Concentration of A at different time intervals are given :
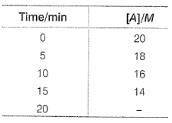
At 20 min, rate will be
For the first order reaction with, C0 as the initial concentration and C at time t, (C0 - C) =
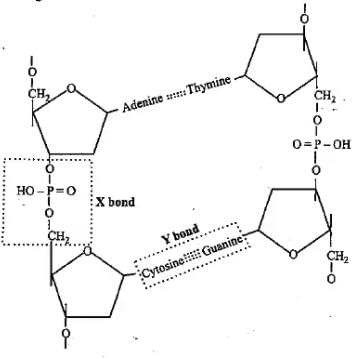
In a DNA molecule, the phosphate group is attached to ____carbon of the sugar residue of its own nucleotide and _____ carbon of the sugar residue of the next nucleotide by ____bonds.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Hemoglobin is an example of quatenary structure of proteins.
Statement 2 : Hemoglobin molecule is composed of four polypeptide chains-two α-chains and two β-chains.
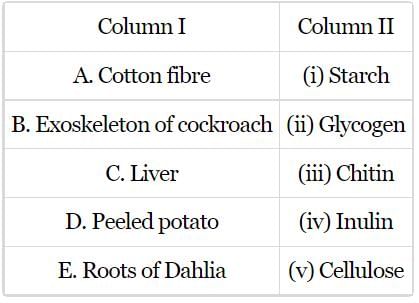
Match Column-I with Column-II and select the correct option from the codes given.
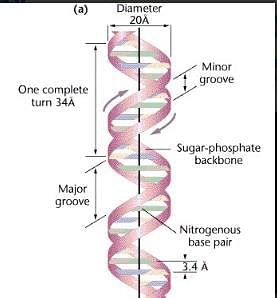
B-DNA which is right-handed double helix contains ______ base pairs per turn of the helix and each turn is _______ long.
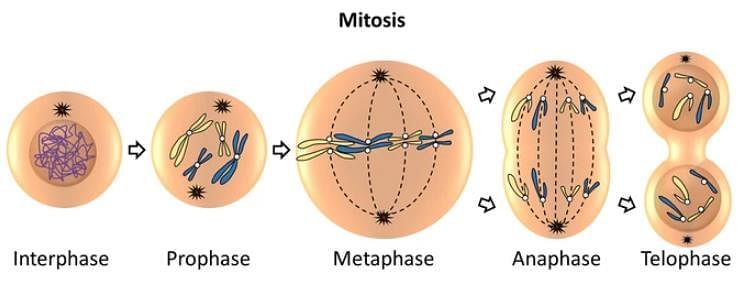
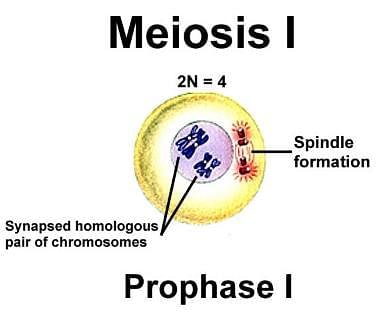
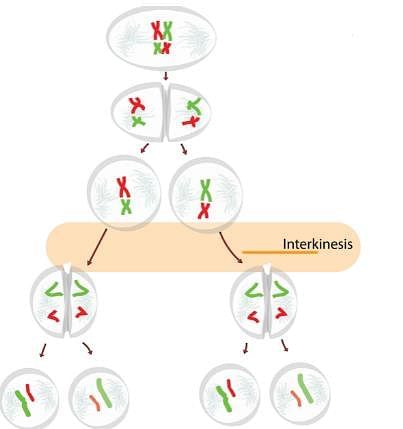
The transition period between M- phase I and M- phase II without DNA replication
During which stage do the chromatids of a bivalent become distinct?
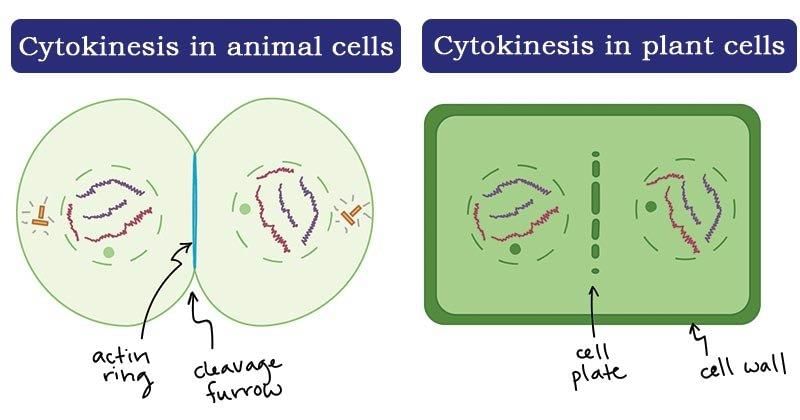
In some lower plants and social insects, the haploid cells are divided by
|
440 videos|1595 docs|542 tests
|