CTET Practice Test: Child Pedagogy-1 - CTET & State TET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Child Development and Pedagogy for CTET Preparation - CTET Practice Test: Child Pedagogy-1
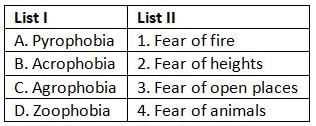
Which of the following factors will not lead to educational backwardness?
Which of the following methods is most suitable for learning disabled children?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
"Creative thinking involves new forms of thinking away from the traditional forms. Thus, creativity includes curiosity, imagination, research, novelty and invention." Who said this?
According to Lubart, which of the following is not a confluence of distinct resource?
Which of the following is the most effective Mode of Teaching- Learning
Who said this, "A child is gifted, if he is either socially talented, mechanically talented, artistically talented, musically talented, linguistically talented, academically talented"?
Which of the following is an important cause of educational backwardness at primary level of education in India?
Which of the following is not among the four psychological states for developing creativity?
Who among the following used the term 'backwardness' in his book?
Who said this, "Backward child is one, who compared with other pupils of the same chronological age shows marked educational deficiency"?
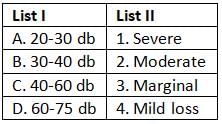
The range of 30-40 db lies in which of the following?
In order to improve work habits of learning disabled, what should be done?
Learning disabled children perform very poorly in
Which of the following statements is not true?
Moderate hearing impairment lies in the db level of
Who said this, 'Backward child is one who in mid-school carrer is unable to do the work of the class next below, which is normal for his age'?
|
68 videos|63 docs|36 tests
|
|
68 videos|63 docs|36 tests
|