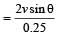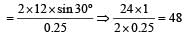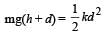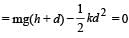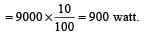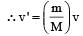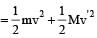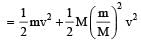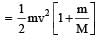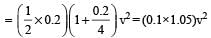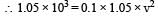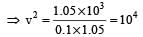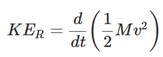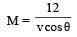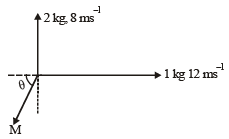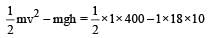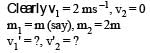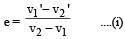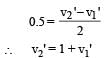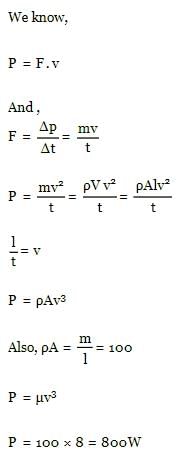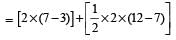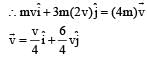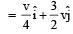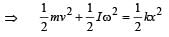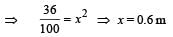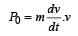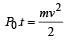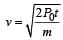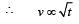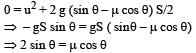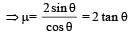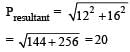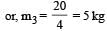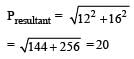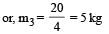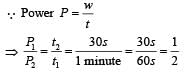31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Work, Energy & Power - 1 - NEET MCQ
23 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Work, Energy & Power - 1
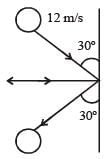
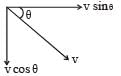
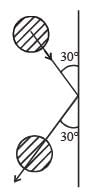
A 0.5 kg ball moving with speed of 12 m/s strikes a hard wall at an angle of 30° with the wall. It is reflected with the same speed and at the same angle. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.25 seconds, the average force acting on the wall is[2006]

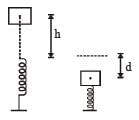
A vertical spring with force constant k is fixed on a table. A ball of mass m at a height h above the free upper end of the spring falls vertically on the spring so that the spring is compressed by a distance d. The net work done in the process is [2007]
Water falls from a height of 60 m at the rate of 15 kg/s to operate a turbine. The losses due to frictional force are 10% of energy. How much power is generated by the turbine?( g = 10 m/s2) [2008]
A shell of mass 200 gm is ejected from a gun of mass 4 kg by an explosion that generates 1.05 kJ of energy. The initial velocity of the shell is:
An engine pumps water continuously through a hose. Water leaves the hose with a velocity v and m is the mass per unit length of the water jet. What is the rate at which kinetic energy is imparted to water? [2009]
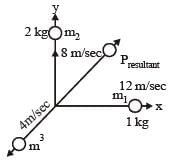
An explosion blows a rock into three parts. Two parts go off at right angles to each other. These two are, 1 kg first part moving with a velocity of 12 ms–1 and 2 kg second part moving with a velocity of 8 ms–1. If the third part flies off with a velocity of 4 ms–1, its mass would be: [2009]
A body of mass 1 kg is thrown upwards with a velocity 20 m/s. It momentarily comes to rest after attaining a height of 18 m. How much energy is lost due to air friction? (g = 10 m/s2)
A ball moving with velocity 2 m/s collides head on with another stationary ball of double the mass. If the coefficient of restitution is 0.5, then their velocities (in m/s) after collision will be:
An engine pumps water through a hose pipe.Water passes through the pipe and leaves it with a velocity of 2 m/s. The mass per unit length of water in the pipe is 100 kg/m. What is the power of the engine? [2010]
The potential energy of a system increases if work is done [2011]
A body projected ver tically fr om the ear th reaches a height equal to earth's radius before returning to the earth. The power exerted by the gravitational force is greatest [2011]
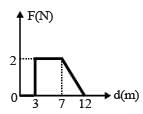
Force F on a particle moving in a straight line varies with distance d as shown in the figure.The work done on the particle during its displacement of 12 m is [2011]
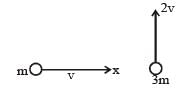
A mass m moving horizontally (along the x-axis) with velocity v collides and sticks to mass of 3m moving vertically upward (along the y-axis) with velocity 2v. The final velocity of the combination is [2011M]
A solid cylinder of mass 3 kg is rolling on a horizontal surface with velocity 4 ms–1. It collides with a horizontal spring of force constant 200 Nm–1 . The maximum compression produced in the spring will be : [2012]
Two spheres A and B of masses m1 and m2 respectively collide. A is at rest initially and B is moving with velocity v along x-axis. After collision B has a velocity v/2 in a direction perpendicular to the original direction. The mass A moves after collision in the direction.
A car of mass m starts from rest and accelerates so that the instantaneous power delivered to the car has a constant magnitude P0. The instantaneous velocity of this car is proportional to : [2012M]
A uniform force of 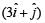 newton acts on a particle of mass 2 kg. The particle is displaced from position
newton acts on a particle of mass 2 kg. The particle is displaced from position 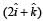 meter to position
meter to position 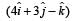 meter. The work done by the force on the particle is [NEET 2013]
meter. The work done by the force on the particle is [NEET 2013]
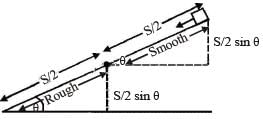
The upper half of an inclined plane of inclination θ is perfectly smooth while lower half is rough.
A block starting from rest at the top of the plane will again come to rest at the bottom, if the coefficient of friction between the block and lower half of the plane is given by [NEET 2013]
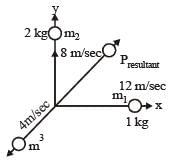
An explosion breaks a rock into three parts in a horizontal plane. Two of them go off at right angles to each other. The first part of mass 1 kg moves with a speed of 12 ms–1 and the second part of mass 2 kg moves with speed 8 ms–1. If the third part flies off with speed 4 ms–1 then its mass is [NEET 2013]
An explosion breaks a rock into three parts in a horizontal plane. Two of them go off at right angles to each other. The first part of mass 1 kg moves with a speed of 12 ms–1 and the second part of mass 2 kg moves with speed 8 ms–1. If the third part flies off with speed 4 ms–1 then its mass is [NEET 2013]
A person holding a rifle (mass of person and rifle together is 100 kg) stands on a smooth surface and fires 10 shots horizontally, in 5 s.Each bullet has a mass of 10 g with a muzzle velocity of 800 ms–1. The final velocity acquired by the person and the average force exerted on the person are [NEET Kar. 2013]
A particle with total energy E is moving in a potential energy region U(x). Motion of the particle is restricted to the region when [NEET Kar. 2013]
One coolie takes 1 minute to raise a suitcase through a height of 2 m but the second coolie takes 30 s to raise the same suitcase to the same height. The powers of two coolies are in the ratio of [NEET Kar. 2013]