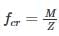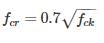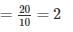Test: Concrete Technology- 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Mock test series of SSC JE Civil Engineering 2025 - Test: Concrete Technology- 2
The amount of iron oxide in white Portland cement is limited to
The diameter of needle used in Vicat’s apparatus for the determination of initial setting time is prescribed as
The initial setting time of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) is:
The approximate ratio of strength of 15 cm cube to that of 15 cm x 30 cm concrete cylinder of the same concrete is
UPV method in non-destructive testing for concrete is used to determine
1. Compressive strength
2. Existence of voids
3. Tensile strength
4. Static modulus of concrete
5. Dynamic modulus of concret
For improvement of workability of concrete, the shape of aggregate recommended is
The diameter of the pipeline used for transportation of concrete by pumps should not exceed:
The process of removing the irregularities from the surface of concrete left after screeding is called
The durability of cement concrete is usually improved by the addition of:
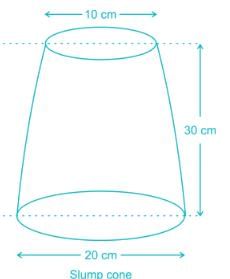
The value of slump commonly adopted for the various concrete mixers are given below.
1. Concrete for road works: 20 to 28 mm
2. Ordinary RCC works: 50 to 100 mm
3. Columns retaining walls: 12 to 25 mm
4. Mass concrete: 75 to 175 mm
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
To determined the modulus of rupture, the size for test specimen used is
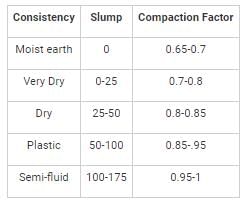
Workability of concrete can be measured using slump, compaction factor and Vee-bee time. Consider the following statements for workability of concrete:
(i) As the slump increases, the Vee-bee time increases.
(ii) As the slump increases, the compaction factor increases.
Which of the following is TRUE?
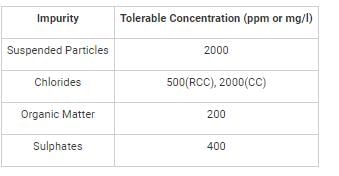
The upper limit of suspended particles in water for the preparation of concrete is:
The ratio of bottom diameter to top diameter of the steel mould used for slump test is:
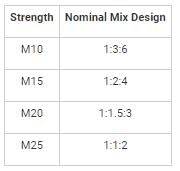
Generally the ratio of different ingredients (Cement Sand and aggregate) in concrete mix of grade M10 is:
Which one of the following is not required in concrete mix – design?
To prevent segregation, the maximum height for placing concrete is:
|
1 videos|1 docs|64 tests
|
|
1 videos|1 docs|64 tests
|