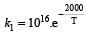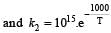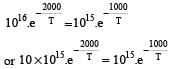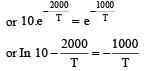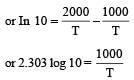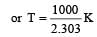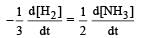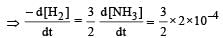31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Chemical Kinetics - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Chemical Kinetics
Half life period of a first-order reaction is 1386 seconds. The specific rate constant of the reaction is: [2009]
For the reaction A + B → products, it is observed that: [2009]
(1) On doubling the initial concentration of A only, the rate of reaction is also doubled and
(2) On doubling the initial concentrations of both A and B, there is a change by a factor of 8 in the rate of the reaction.
The rate of this reaction is given by:
(1) On doubling the initial concentration of A only, the rate of reaction is also doubled and
(2) On doubling the initial concentrations of both A and B, there is a change by a factor of 8 in the rate of the reaction.
The rate of this reaction is given by:
For the reaction 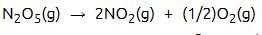 the value of rate of disappearance of N2O5 is given as 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1s–1. The rate of formation of NO2 and O2 is given respectively as : [2010]
the value of rate of disappearance of N2O5 is given as 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1s–1. The rate of formation of NO2 and O2 is given respectively as : [2010]
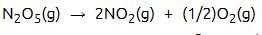 the value of rate of disappearance of N2O5 is given as 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1s–1. The rate of formation of NO2 and O2 is given respectively as : [2010]
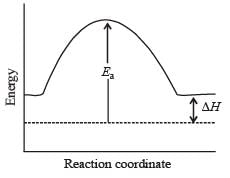
the value of rate of disappearance of N2O5 is given as 6.25 × 10–3 mol L–1s–1. The rate of formation of NO2 and O2 is given respectively as : [2010]For an endothermic reaction, energy of activation is Ea and enthalpy of reaction of ΔH (both of these in kJ/mol). Minimum value of Ea will be. [2010]
During the kinetic study of the reaction, 2A + B → C + D, following results were obtained:
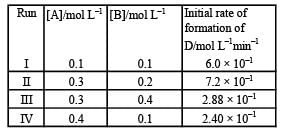
Based on the above data which one of the following is correct? [2010]
The rate of the reaction 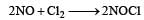 is given by the rate equation rate = k [NO]2 [Cl2] [2010] The value of the rate constant can be increased by:
is given by the rate equation rate = k [NO]2 [Cl2] [2010] The value of the rate constant can be increased by:
Which one of the following statements for the order of a reaction is incorrect ? [2011]
For the reaction 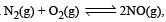 , the equilibrium constant is K1. The equilibrium constant is K2 for the reaction [2011]
, the equilibrium constant is K1. The equilibrium constant is K2 for the reaction [2011] 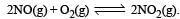 .What is K for the reaction
.What is K for the reaction 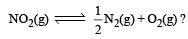
The rate of the reaction 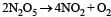 can be written in three ways :
can be written in three ways :
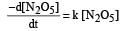
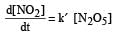
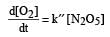
The relationship between k and k' and between k and k"are :
[2011 M]
The unit of rate constant for a zero order reaction is [2011 M]
In a reaction, A + B → Product, rate is doubled when the concentration of B is doubled, and rate increases by a factor of 8 when the concentrations of both the reactants (A and B) are doubled rate, law for the reaction can be written as : [2012]
In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become : [2012]
Activation energy (Ea) and rate constants (k1 and k2) of a chemical reaction at two different temperatures (T1 and T2) are related by : [2012 M]
What is the activation energy for a reaction if its rate doubles when the temperature is raised from 20°C to 35°C? (R = 8.314 J mol–1 K–1) [NEET 2013]
A reaction having equal energies of activation for forward and reverse reaction has : [NEET 2013]
A reaction is 50% completed in 2 hours and 75% completed in 4 hours. The order of reaction is [NEET Kar. 2013]
For a reaction between A and B the order with respect to A is 2 and the order with respect to B is 3. The concentrations of both A and B are doubled, the rate will increase by a factor of: [NEET Kar. 2013]
For an exothermic reaction, the energy of activation of the reactants is [1994]
In a reaction, A + B → Product, rate is doubled when the concentration of B is doubled, and rate increases by a factor of 8 when the concentrations of both the reactants (A and B) are doubled, rate law for the reaction can be written as
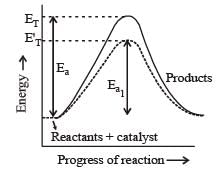
Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by [1998]
In the following reaction , how is the rate of appearance of the underlined product related to the rate of disappearance of the underlined reactant ? [2000]
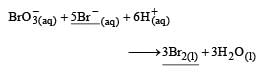
When a biochemical reaction is carried out in laboratory in the absence of enzyme then rate of reaction obtained is 10–6 times, then activation energy of reaction in the presence of enzyme is
For the reaction 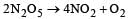 rate and rate constant are 1.02 × 10–4 mol lit–1 sec–1 and 3.4 × 10–5 sec–1 respectively then concentration of N2O5 at that time will be [2001]
rate and rate constant are 1.02 × 10–4 mol lit–1 sec–1 and 3.4 × 10–5 sec–1 respectively then concentration of N2O5 at that time will be [2001]
 , rate of reaction
, rate of reaction 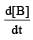 is equal to
is equal to
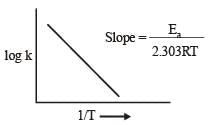
The temperature dependence of rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction is written in terms of Arrhenius equation, 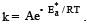 . Activation energy
. Activation energy 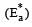 of the reaction can be calculated by plotting [2003]
of the reaction can be calculated by plotting [2003]
If the rate of the reaction is equal to the rate constant, the order of the reaction is [2003]
For the reaction 2A + B → 3C + D which of the following does not express the reaction rate ? [2006]
The reaction of hydrogenandiodine monochloride is given as: [2007]
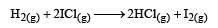
The reaction is of first order with respect to H2(g) and ICI(g), following mechanisms were proposed.
Mechanism A:
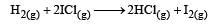
Mechanism B:
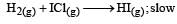
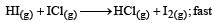
Which of the above mechanism(s) can be consistent with the given information about the reaction?
The rate constants k1 and k2 for two different reactions are 1016 . e–2000/T and 1015 . e–1000/T, respectively. The temperature at which k1 = k2 is :
For the reaction, 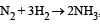 , [2009]
, [2009]
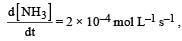 the value of
the value of
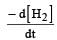 would be dt:
would be dt:
|
108 videos|287 docs|122 tests
|


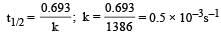

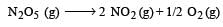
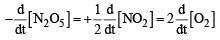
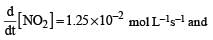
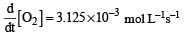
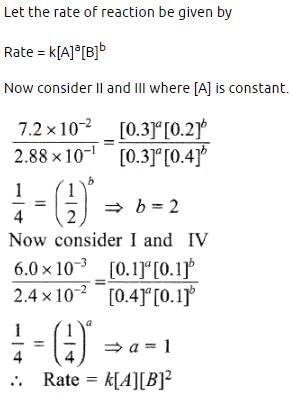
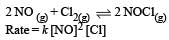
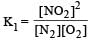
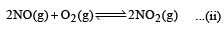
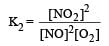
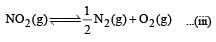
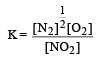
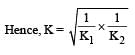
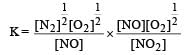
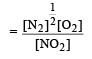
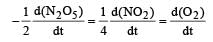
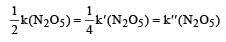
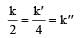
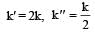
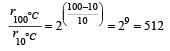
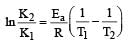
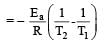
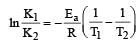
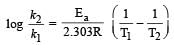
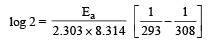
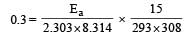
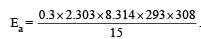
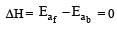
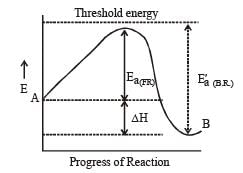


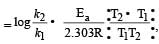 where k1 is the rate constant at temperature T1 and k2 is the rate constant at temperature T2 and Ea is the activation energy. Therefore activation energy of chemical reaction is determined by evaluating rate constant at two different temperatures.
where k1 is the rate constant at temperature T1 and k2 is the rate constant at temperature T2 and Ea is the activation energy. Therefore activation energy of chemical reaction is determined by evaluating rate constant at two different temperatures.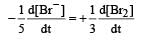
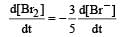
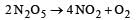
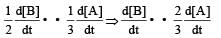
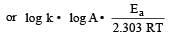
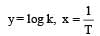
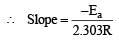
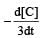 will not represent the reaction rate. It should not have –ve sign as it is product. since
will not represent the reaction rate. It should not have –ve sign as it is product. since 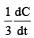 show the rate of formation ofproduct C which will be positive.
show the rate of formation ofproduct C which will be positive.