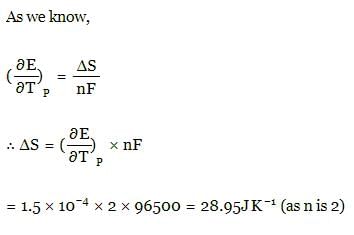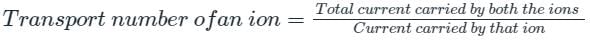Test: Electrochemistry - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Electrochemistry - 2
A 19th century iron bridge is protected from corrosion by connecting it to a block of metal (sacrificial anode), which is replaced annually. The corrosion of iron, represented by the chemical equation:
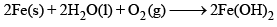
Which of the following metals is best suited as sacrificial anode:
Consider the following electrochemical cell, from which current is drawn through an external resistor of 10 Ohms. During this process, the concentration of CuSO4 in the left and the right halfcells were measured, and the value of 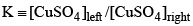 was calculated. From the init ial value of K = 10, predict the value of K after a very long time when the cell stopped giving any current.
was calculated. From the init ial value of K = 10, predict the value of K after a very long time when the cell stopped giving any current.
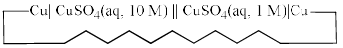
The velocity of Li+ ion in water is 2 × 10–2 cm/sec when 100 V is applied between two electrodes separated by 2 cm. The mobility of Li+ ion in water is,
At 20°C, the standard EMF of a certain cell is +0.2699 V, and at 30°C it is + 0.2669 V. What can you say about the standard entropy of this reaction? Assume that the standard ΔH° and ΔS° are independent of temperature:
The cell potential for the following electrochemical system at 25°C is:
Al(s) | Al3+ (0.01 M) || Fe2+ (0.1 M) | Fe (s)
Given: Standard reduction potential of Al3+ + 3e– → Al is –1.66 V at 25°C
Standard reduction potential of Fe2+ + 2e– → Fe is –0.44 V at 25°C
FAD is a redox active molecule which takes part in many important biological reactions. the redox potential of FAD at pH 7.0 is given below:
Calculate the redox potential when the media is acidified to pH0
According to the Nernst equation, the potential of an electrode changes by 59.2 mV whenever the ratio of the oxidized and the reduced species changed by a factor of 10 at 25°C. What would be the corresponding change in the electrode potential if the experiment is carried out at 30°C:
Chemical oxidizing of water to produce O2 gas is an energy demanding reaction, done routinely by plants using the process called photosynthesis. By how many eV will it be uphill if the water oxidation reaction be carried out at pH = 0 versus at pH = 7.0:
The concentration of K+ ion inside a biological cell is 20 times higher than outside. The magnitude of potential difference between the two sides is [Given: 2.303 RT/F = 59 mV]
If the transport number of Na+ is 0.463 (dilute solution of NaCl in methanol), the transport number of H+ (dilute solut ion of HCl in methanol) is:
(Given, (NaCl in methanol) = 96.9 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 and
(HCl in methanol) = 192 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1
The molality of (NH4)2SO4 solution that has the same ionic strength as 1 mol kg–1 solution of KCl is:
A concentration cell with two hydrogen electrodes at two different pressure is depicted as
The potential (Ecell) of the cell is
The molar conductivity of 0.009 M aqueous solution of a weak acid (HA) is 0.005 Sm2mol-1 and the limiting molar conductivity of HA is 0.05 Sm2mol-1 at 298 K. Assuming activity coefficients to be unity, the acid dissociation constant (Ka) of HA at this temperature is
The efficiency of a cell is 60%. Its cell reaction is:
The standard electrode potential of cell is:
The temperature coefficient for a given cell is 1.5 × 10–4 JK–1 at 300 K. The change in entropy during cell reaction:
For the following electrochemical cell at 298 K,
Pt(s) | H2 (g, 1 bar) | H+ (aq, 1 M) || M4+ (aq, M2 (aq)| Pt (s)
The value of x is:
At infinite dilut ion, eachion of an electrolyte contributes a characteristic ionic conductance towards equivalent conductance of electrolyte which is independent of the nature of other ion present in solution. This statement was given by:
Which one of the following solutions has lowest conducting power:
The fraction of the total current carried by an ion is known as:
At pH = 2, E°Quinhydrone = 1.30 V, EQuinhydrone will be:
The time required to coat a metal surface of 80 cm2 with 5 × 10–3 cm thick layer of silver (density 1.05 g cm–3) with the passage of 3A current through a silver nitrate solution is:
A hydrogen electrode placed in a buffer solution of CH3COONa and acetic acid in the ratio’s x : y and y : x has electrode potential values E1 volts and E2 volts respectively at 25°C. The pKa values of acetic acid is (E1 and E2 are oxidation potential)
Salts of A (atomic weight 7), B (atomic weight 27) and C (atomic weight 48) were electrolyzed under identical condition using the same quantity of electricity. It was found that when 2.1 g of A was deposited, the weights of B and C deposited were 2.7g and 7.2 g. The valencies of A, B and C respectively:
The conductance of a solution of an electrolyte is same as that of its conductivity. The cell used can be said to have cell constant equal to:
The value of molar conductance of HCl is greater that of NaCl at particular temperature and dilution because:
The factors, which influence the conductance of solution are:
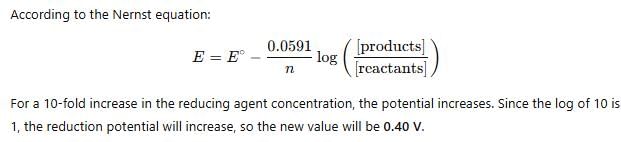
The reduction potential of a half-reaction is E∘=+0.34 V. If the concentration of the reducing agent is increased by a factor of 10, what is the new reduction potential at 25°C?
|
75 videos|339 docs|78 tests
|