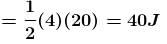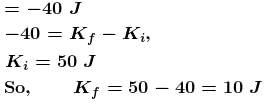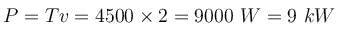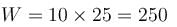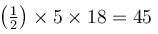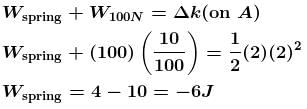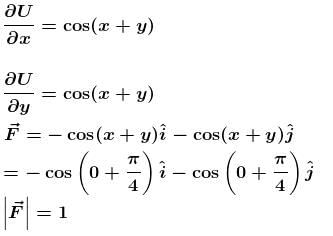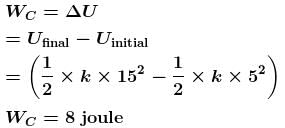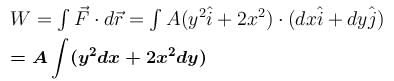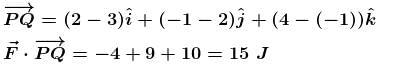Work, Power And Energy NAT Level - 1 - Physics MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic wise Tests for IIT JAM Physics - Work, Power And Energy NAT Level - 1
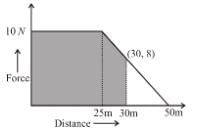
The graph between the resistive force F acting on a body and the distance covered by the body is shown in the figure. The mass of the body is 25kg and initial velocity is 2m/s. When the distance covered by the body is 4m, its kinetic energy (in Joule) would be :


A particle moves with a velocity 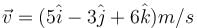 under the influence of a constant force
under the influence of a constant force  The instantaneous power (in Js–1) applied to the particle is :
The instantaneous power (in Js–1) applied to the particle is :
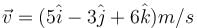 under the influence of a constant force
under the influence of a constant force  The instantaneous power (in Js–1) applied to the particle is :
The instantaneous power (in Js–1) applied to the particle is :An electric motor creates a tension of 4500N in hoisting cable and reels it at the rate of 2m/s. What is the power of electric motor in kW?
A body of mass 5kg is acted upon by a variable force. The force varies with the distance covered by the body. Find the kinetic energy (in Joule) of the body when the body has covered 30m distance? Assume that the body starts from rest.
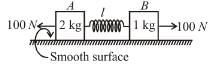
In the figure shown initially spring is in unstretched state and blocks are at rest. Now 100N force is applied on block A and B as shown in figure. After some time velocity of A becomes 2m/s and that of B 4m/s and block A displaced by amount 10cm and spring is stretched by amount 30cm. Then work done by spring force on A will be (in Joule) :
The potential energy for a force field 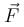 is given by U(x,y) = sin(x + y). The force acting on the particle of mass m at
is given by U(x,y) = sin(x + y). The force acting on the particle of mass m at 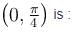
A spring of force constant 800N/m has an extension of 5cm. The work done (in Joule) in extending it from 5cm to 15cm is :
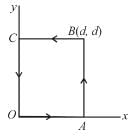
The work done by the force  where A is a constant and x and y in meters around the path shown is :
where A is a constant and x and y in meters around the path shown is :
Take, A = 50N/m and d = 2.
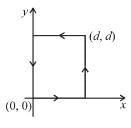
An object is moving along a straight line path from P to Q under the action of a force 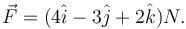 If the co-ordinate of P and Q in metres are (3, 2, –1) and (2,-1,4) respectively. Then the work done by the force in Joule is :
If the co-ordinate of P and Q in metres are (3, 2, –1) and (2,-1,4) respectively. Then the work done by the force in Joule is :
Power supplied to a particle of mass 2kg varies with time as P = 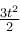 watt. Here t is time in second. If velocity of particle at t =0sec is v = 0m/s. The velocity of particle (in ms-1) at time t = 2sec will be :
watt. Here t is time in second. If velocity of particle at t =0sec is v = 0m/s. The velocity of particle (in ms-1) at time t = 2sec will be :