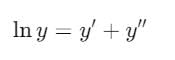Differential Equations - 1 - Mathematics MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise Tests & Solved Examples for Mathematics - Differential Equations - 1
Let k be real constant. The solution of the differential equations 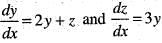 satisfies the relation
satisfies the relation
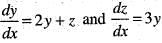 satisfies the relation
satisfies the relationFind the General Solution of the given differential equation.
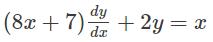
Consider the differential equation 2 cos (y2)dx - xy sin (y2)dy = 0
If the general solutions of a differential equation are (y + c)2 = cx, where c is an arbitrary constant, then the order and degree of differential equation is
The general solution of 
(Here c1 and c2 are arbitrary constants.)
Let y1(x) and y2(x) be linearly independent solution of the differential equation y" + P(x) y' + Q(x)y = 0, where P(x) and Q(x) are continuous functions on an interval I. Then y3(x) = ay1(x) + by2(x) and y4(x) = cy1(x) dy2(x) are linearly independent solutions of the given differential equations if
Consider the differential equations, satisfying y(0) = 0, 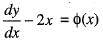 where
where 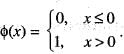 This initial value problem
This initial value problem
The particular integral of the differential equation
y" + y' + 3y = 5 cos(2x + 3) is
The general solution of differential equation
4x2y" - 8xy' + 9y = 0 is
What is the order of the non-homogeneous partial differential equation,
If g(x, y)dx + (x + y )dy = 0 is an exact differential equation and if g(x, 0) = x2, then the general solution of the differential equation is
Consider the differential equation dy/dx = ay - by2, where a, b > 0 and y(0) = y0. As x → + ∝, the solution y (x) tends to
Orthogonal trajectories of the family of curves (x - 1)2 + y2 + 2ax = 0 are the solution of the differential equation
The solution of differential equation 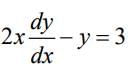 represents the family of
represents the family of
Let 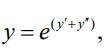 then sum of degree and order of given ordinary differential equation is
then sum of degree and order of given ordinary differential equation is
|
27 docs|150 tests
|


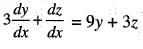
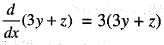


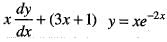 is
is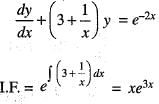

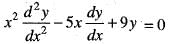
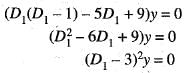
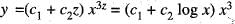

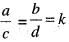
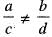
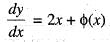
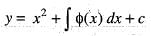
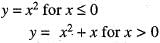
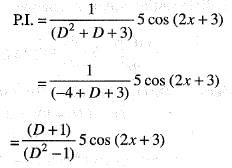
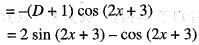
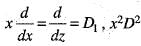
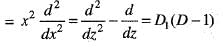




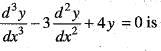
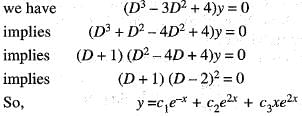
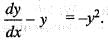 Then
Then 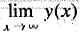 is equal to
is equal to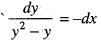
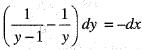
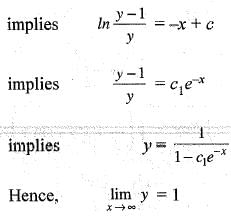
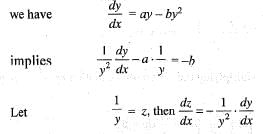

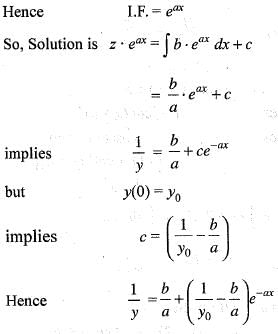
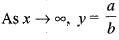
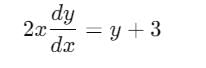
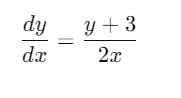
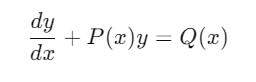
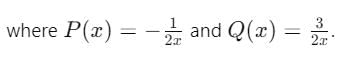
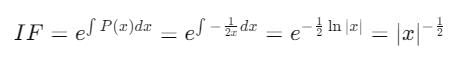
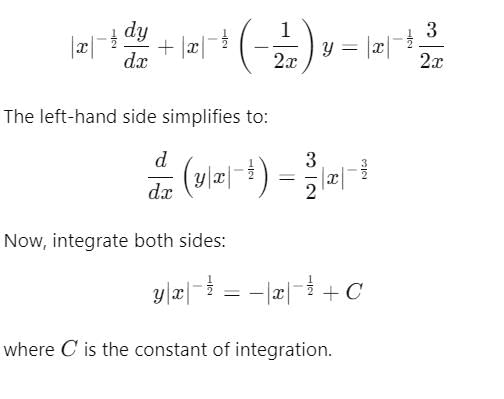
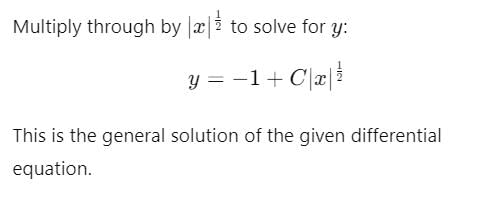
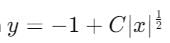 represents a family of parabolas. This is because the equation has the form of a quadratic curve (which describes a parabola).
represents a family of parabolas. This is because the equation has the form of a quadratic curve (which describes a parabola).