Test: Matrix - Mathematics MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise Tests & Solved Examples for Mathematics - Test: Matrix
The rank of a 3 x 3 matrix C (=AB), found by multiplying a non-zero column matrix A of size 3 x 1 and a non-zero row matrix B of size 1 x 3, is
A is a 3 x 4 real matrix and A x = b is an inconsistent system of equations. The highest possible rank of A is
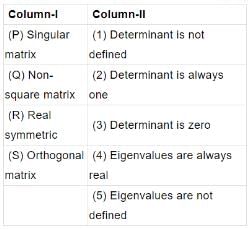
[A] is a square matrix which is neither symmetric nor skew-symmetric and [A]T is its transpose. The sum and difference of these matrices are defined as [S] = [A] + [A]T and [D] = [A] -[A]T, respectively. Which of the following statements is True?
Real matrices [A]3 x 1, [B]3 x 3, [C]3 x 5,[D]5 x 3, [E]5 x 5 and [F]5 x 1 are given. Matrices [B] and [E] are symmetric.
Following statements are made with respect to these matrices.
1. Matrix product [F]T [C]T [B] [C] [F] is a scalar.
2. Matrix product [D]T [F] [D] is always symmetric.
With reference to above statements, which of the following applies?
Consider the matrices X (4 × 3), Y (4 × 3) and P (2 × 3). The order or P (XTY)–1PT] T will be
|
27 docs|150 tests
|


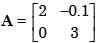 and A–1 =
and A–1 = 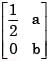 Then (a + b) =
Then (a + b) =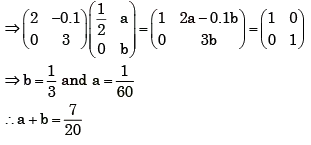
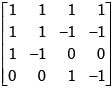 [AAT]-1 is
[AAT]-1 is 
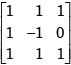 is
is 
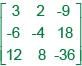
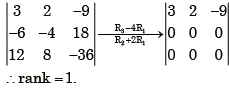
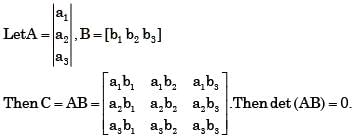
 the rank of the matrix is
the rank of the matrix is
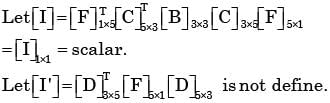
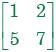 is,
is,