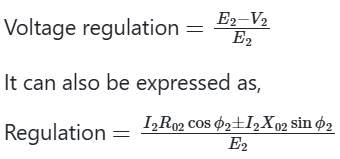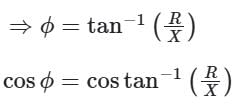Test: Parallel Operation of Single-Phase Transformers - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Electrical Machines - Test: Parallel Operation of Single-Phase Transformers
Transformer operating in parallel will share a common load in the best possible manner if
A 2000/1000/500 three winding transformer is to be used as auto transformer with supply of 3000 V. Two loads of 1050 kVA at 3500V,and other one at 180 kVA at 1000V. The total kVA supplied will be
Which if the conditions is must be fulfilled for a satisfactory parallel operation of transformers?
A. Positive sequence components – 5th harmonic component
B. Negative sequence components – 7th harmonic component
C. Zero sequence components – 3rd harmonic component
Above are the matching made for the harmonics and the associated harmonic component, then the correct marking is
Two single phase transformers A and B are operating in parallel having same impedance. But the x/r ratio of them are not equal. Then total kVA output of the output will be
Two single phase transformers A and B are operating in parallel having same impedance. But the x/r ratio of them are not equal and xa > xb. Then
Two single phase transformers A and B are operating in parallel having different impedance and identical x/r ratio. Also impedance of A is more than that of B,then
Operating transformers in parallel gives the advantage of
In a transformer, the load current is kept constant, while the power factor is varied. Under this situation, zero voltage regulation will be observed
A single-phase, 2 kVA, 100/200 V transformer is reconnected as an auto-transformer such that its kVA rating is maximum. The new rating, in kVA, is ______.
|
20 videos|123 docs|26 tests
|