Test: Electrocardiogram & Circulatory Pathways (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - Test: Electrocardiogram & Circulatory Pathways (NCERT)
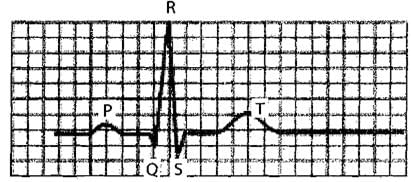
In ECG, P-R interval corresponds to
The given figure is the ECG of a normal human. Which one of its components is correctly interpreted below

Which of the following statements is correct?
Which of the following is the diagrammatic representation of standard electrocardiogram(ECG)?
In a standard ECG which one of the following alphabets is the correct representation of the respective activity of the human heart?
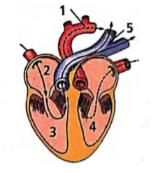
In the given figure of the heart which of the labelled part (1,2,3,4,5) carries oxygenated blood?
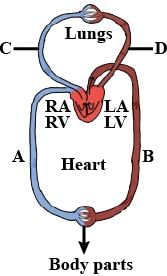
Choose the schematic diagram which properly respresents pulmonary circulation in humans.
Which of the following sequences is truly a systemic circulation pathway?
What is the nature of blood passing through blood vessels A, B, C and D respectively?
To measure ECG, usually how many electrodes are connected to a patient?
|
169 videos|531 docs|136 tests
|



















