Test: Locomotion & Movement - 2 - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - Test: Locomotion & Movement - 2
What is the type of movable joint present between the atlas and axis?
The property which doesn’t belong to muscle fibres is :
Polymerisation of actin monomers involves ATP hydrolysis as shown in the following figure : [choose the correct one]
How many regions is the vertebral column divided into?
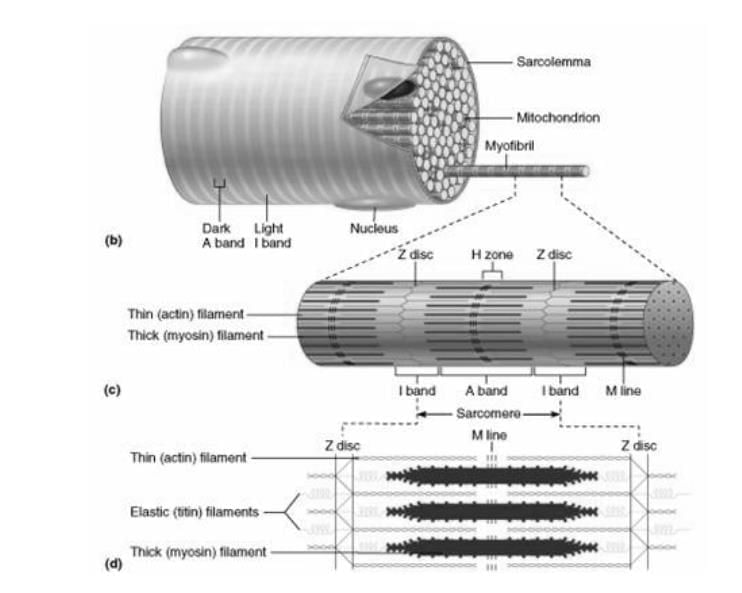
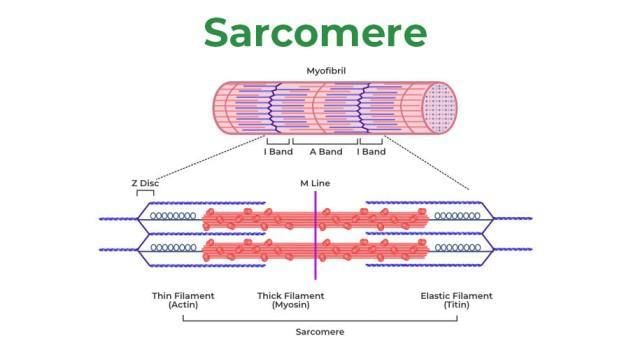
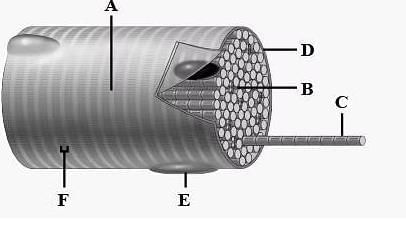
The diagram given below represnts the histology of a striped muscle. Label the parts A,B,C,D,E and F
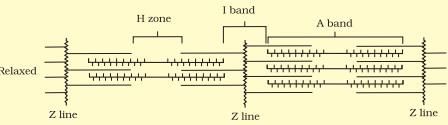
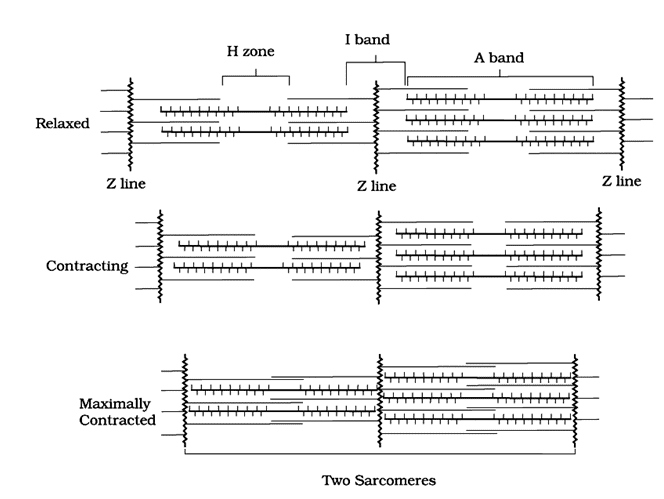
Look at the following figure of movement of the thin filaments
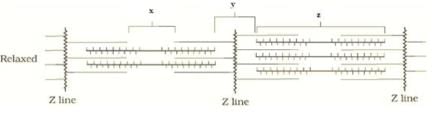
The label x, y, and z are respectively
Each pectoral girdle :
i. has 2 pairs of bones, a pair of clavicle and a pair of scapula.
ii. scapula contains expanded process and glenoid cavity, the latter is for articulation of the head of humerus.
Which disorder is caused due to wild contractions in muscles?
Read the following statements about muscle contraction in humans :
i. chemical energy is converted into mechanical energy during muscle contraction and the chemical is a neurotransmitter.
ii. a neurotransmitter acetylcholine at motor end plate converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
iii. in a contracted muscle, volume remains the same.
iv. a contracted muscle becomes shorter and thicker.
During vigorous exercise :
i. lactic acid accumulates in muscle cells to meet its energy needs immediately.
ii. lactic acid is formed by anaerobic respiration hence oxygen consumption by muscles is reduced.
iii. This reduction in oxygen consumption is called oxygen debt of muscle.
Which of the following statement is Correct ?
Myasthenia gravis leads to fatigue and weakness. It is not :
Read the following A to D statements and select the option that contains both correct statements:
A. Z-line is present in the centre of the light band.
B. Thin filaments are firmly attached to the M-line
C. The central part of thick filaments, not overlapped by thin filaments is called Z-band
D. Light band contains only thin filaments
Assertion (A): Red fibres in muscles have a high content of myoglobin, which contributes to their reddish appearance.
Reason (R): These fibres primarily rely on anaerobic metabolism for energy production.
|
180 videos|362 docs|148 tests
|