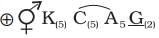Test: Morphology of Flowering Plants - 2 - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - Test: Morphology of Flowering Plants - 2
The arrangement of leaves on a stem is called:
The root is covered at the apex by a thimble-like structure called
Roots developing from plant parts other than radicle are
The form of thalamus in which ovary is at top and stamens, petals and sepals are borne below is called
The part that develops from the plumule of the embryo of a germinating seed is
Match the following terms with their correct descriptions:

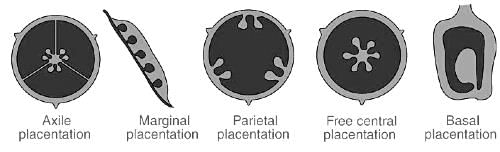
Placentation in a syncarpous, unilocular ovary bearing two or more placentae longitudinally along the wall is called
When the stamens in a flower remain free, it is said to be
Which of the following correctly describes the floral formula of the Solanaceae family, commonly known as the 'potato family'?
Assertion: A flower that can be divided into two similar halves in one particular vertical plane is actinomorphic.
Reason: Actinomorphic flowers exhibit radial symmetry, which allows division into two equal halves along any radial plane.
What is the structure of a typical stamen in the androecium of a flowering plant?
|
169 videos|531 docs|136 tests
|