Test: Muscular System - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 11 - Test: Muscular System
Assertion (A): Myasthenia gravis is primarily characterized by the rapid degeneration of skeletal muscle fibers.
Reason (R): Myasthenia gravis affects the neuromuscular junction, leading to fatigue and weakness in skeletal muscles.
Reason (R): Myasthenia gravis affects the neuromuscular junction, leading to fatigue and weakness in skeletal muscles.
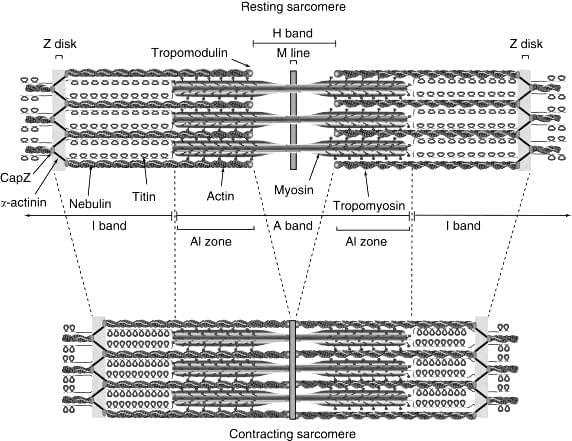
Choose the letter from the figure that most appropriately corresponds to the structure:
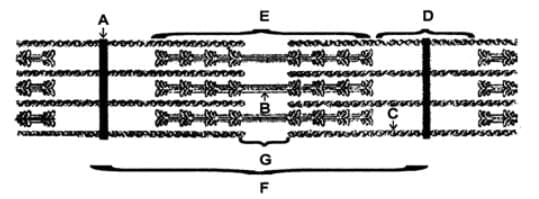
I.A-band II. I-band III. Sarcomere IV. H-zone
V.Myosin VI.Actin, Troponin, Tropomyosin VII. Z –line
Which of these structures has alternate dark and light bands on it?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Muscle contraction begins with a signal from the central nervous system transmitted through a motor neuron.
ii. The neuromuscular junction is the site where the motor neuron and muscle fibre communicate.
iii. Calcium ions released into the sarcoplasm directly bind to myosin to initiate contraction.
iv. Troponin plays a critical role in exposing active sites on actin filaments for myosin binding.
Which of the following statements regarding muscle structure and contraction are correct?
i. The light bands in muscle fibers, known as I-bands, contain actin filaments.
ii. Cardiac muscles are voluntary muscles controlled directly by the nervous system.
iii. Each functional unit of contraction in a muscle fiber is called a sarcomere, defined by Z-lines.
iv. Myosin filaments are thinner than actin filaments and are referred to as thick filaments.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct regarding the structure and function of actin filaments?
i. Each actin filament is composed of two helically wound 'F' (filamentous) actins.
ii. 'G' (Globular) actins are monomers that polymerize to form 'F' actins.
iii. Tropomyosin runs parallel to the 'F' actins and does not interact with them.
iv. Troponin is attached to tropomyosin at regular intervals and regulates the binding sites for myosin on the actin filaments.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Each myosin filament is composed of many monomeric proteins known as Meromyosins.
ii. The heavy meromyosin (HMM) consists of a tail and a globular head.
iii. The cross arm of the myosin filament projects outwards at a regular distance and angle.
iv. The globular head of myosin serves as an inactive enzyme with no binding sites for ATP.
Assertion (A): Muscle fibers are classified as red and white fibers based on the amount of myoglobin present in them.
Reason (R): Red fibers contain more myoglobin, which enhances their ability to store oxygen and sustain aerobic metabolism.
What sequence of events correctly describes the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction?
|
169 videos|531 docs|136 tests
|