Test: Fourier Series, Numerical Methods & Complex Variables- 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Fourier Series, Numerical Methods & Complex Variables- 2
Choose the function f(t); –∞ < t < ∞, for which a Fourier series cannot be defined.
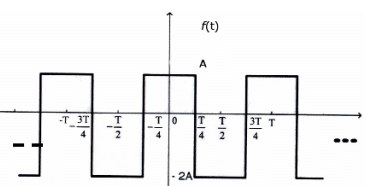
The trigonometric Fourier series for the waveform f(t) shown below contains
Which of the following functions would have only odd powers of x in its Taylor series expansion about the point x = 0?
The Taylor series expansion of
The sum of the infinite series,
The summation of series
Fourier series for the waveform, f (t) shown in fig. is
The Fourier Series coefficients, of a periodic signal x (t), expressed as
are given by
For the function of a complex variable W = ln Z (where, W = u + jv and Z = x + jy), the u = constant lines get mapped in Z-plane as
ii, where i = √−1, is given by
Assuming and t is a real number
The modulus of the complex number
Using Cauchy’s integral theorem, the value of the integral (integration being taken in counter clockwise direction)
Which one of the following is NOT true for complex number Z1and Z2 ?
For the equation, s3 - 4s2 + s + 6 =0
The number of roots in the left half of s-plane will be
The value of the integral of the complex function
Along the path |s| = 3 is
For the function of a complex variable z, the point z = 0 is
The polynomial p(x) = x5 + x + 2 has
If z = x + jy, where x and y are real, the value of |ejz| is
The root mean squared value of x(t) = 3 + 2 sin (t) cos (2t) is
We wish to solve x2 – 2 = 0 by Netwon Raphson technique. Let the initial guess b x0 = 1.0 Subsequent estimate of x(i.e.x1) will be:
The order of error is the Simpson’s rule for numerical integration with a step size h is
The table below gives values of a function F(x) obtained for values of x at intervals of 0.25.
The value of the integral of the function between the limits 0 to 1 using Simpson’s rule is
A differential equation has to be solved using trapezoidal rule of integration with a step size h=0.01s. Function u(t) indicates a unit step function. If x(0-)=0, then value of x at t=0.01s will be given by
Consider the series obtained from the Newton-Raphson method. The series converges to
Given a>0, we wish to calculate its reciprocal value 1/a by using Newton-Raphson method :
for f(x) = 0. For a=7 and starting wkith x0 = 0.2. the first 2 iterations will be
With a 1 unit change in b, what is the change in x in the solution of the system of equations x + y = 2, 1.01 x + 0.99 y = b?
The accuracy of Simpson's rule quadrature for a step size h is
|
29 docs|220 tests
|



















