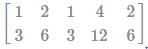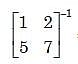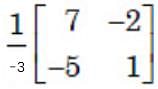Test: Systems of Linear Equations, Matrix Algebra & Transform Theory- 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Systems of Linear Equations, Matrix Algebra & Transform Theory- 1
The system of linear equations
4x + 2y = 7
2x + y = 6 has
4x + 2y = 7
2x + y = 6 has
For the following set of simultaneous equations:
1.5x – 0.5y = 2
4x + 2y + 3z = 9
7x + y + 5z = 10
1.5x – 0.5y = 2
4x + 2y + 3z = 9
7x + y + 5z = 10
The following set of equations has
3 x + 2 y + z = 4
x – y + z = 2
-2 x + 2 z = 5
3 x + 2 y + z = 4
x – y + z = 2
-2 x + 2 z = 5
Consider the system of simultaneous equations
x + 2y + z = 6
2x + y + 2z = 6
x + y + z = 5
This system has
Multiplication of matrices E and F is G. Matrices E and G are
What is the matrix F?
Consider a non-homogeneous system of linear equations representing mathematically an over-determined system. Such a system will be
For the set of equations
x1 + 2x + x3 + 4x4 = 0
3x1 + 6x2 + 3x3 + 12x4 = 0
Let P ≠ 0 be a 3 × 3 real matrix. There exist linearly independent vectors x and y such that Px = 0 and Py = 0. The dimension of the range space of P is
The eigen values of a skew-symmetric matrix are
The rank of a 3×3 matrix C (=AB), found by multiplying a non-zero column matrix Aof size 3×1 and a non-zero row matrix B of size 1×3, is
Match the items in columns I and II.
Column I Column II
P. Singular matrix 1. Determinant is not defined
Q. Non-square matrix 2. Determinant is always one
R. Real symmetric 3. Determinant is zero
S. Orthogonal matrix 4. Eigenvalues are always real
5. Eigenvalues are not defined
Real matrices are given. Matrices [B] and
[E] are symmetric.
Following statements are made with respect to these matrices.
1. Matrix product [F]T [C]T [B] [C] [F] is a scalar.
2. Matrix product [D]T [F] [D] is always symmetric.
With reference to above statements, which of the following applies?
The product of matrices (PQ)–1 P is
The matrix A
=
is decomposed into a product of a lower triangular matrix [L] and an upper triangular matrix [U]. The properly decomposed [L] and [U] matrices respectively are
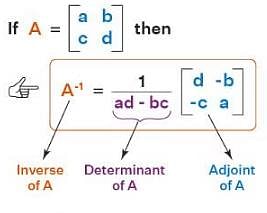
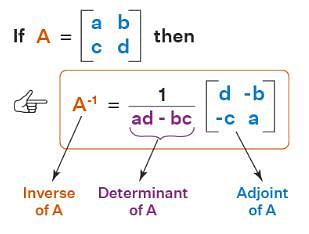
The inverse of the matrix is
The inverse of the 2 × 2 matrix is,
For what value of λ, do the simultaneous equation 2x + 3y = 1, 4x + 6y = λ have infinite solutions?
Given that F(s) is the one-sided Laplace transform of f(t), the Laplace transform of is [EC:
If f(t) is a finite and continuous function for t, the Laplace transformation is given by
For f(t) = cos h mt, the Laplace transformation is…..
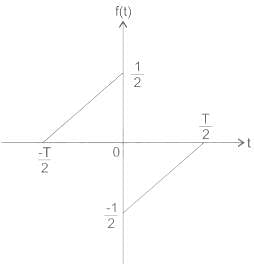
A function f (t) is shown in the figure.
|
29 docs|220 tests
|