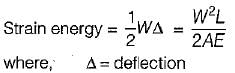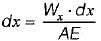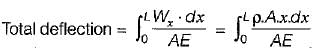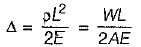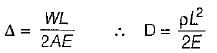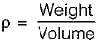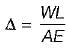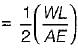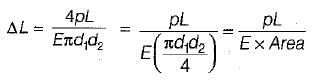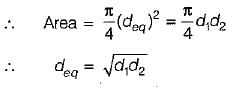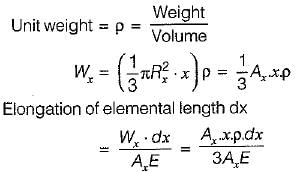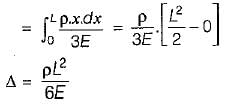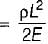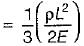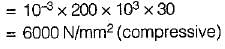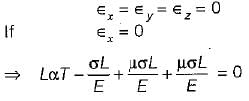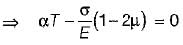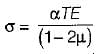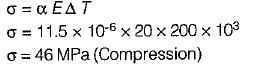Test: Tension, Compression & Shear - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering - Test: Tension, Compression & Shear - 2
A member having length L, cross-sectional area A and modulus of elasticity E is subjected to an axial load W. The strain energy stored in this member is
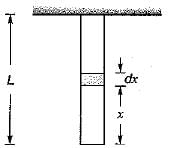
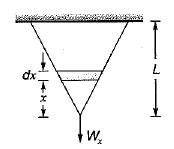
A straight bar having a constant cross-sectional area A, length L and weight W, is hanging vertically. If E is the Young’s modulus of the material of the bar, total increase in length of the bar due to its own weight only will be
A solid metal bar of uniform diameter D and length L is hung vertically from a ceiling. If the density of the material of the bar is p and the modulus of elasticity is E, then the total elongation of the bar due to its own weight is
The deformation of a bar under its own weight as compared to that when subjected to a direct axial load equal to its own weight will be
A tapering bar (diameter of end sections being, d1 and d2) and a bar of uniform cross-section, 'd' have the same length and are subjected to the same axial pull. Both the bars will have the same extension if ‘d’ is equal to
The elongation of a conical bar under its own weight is equal to
A 100 mm x 5 mm steel bar free to expand is heated from 15°C to 40°C. What shall be induced in the bar after heating?
A rod of material with E = 200 x 103 MPa and α = 10-3/°C is fixed at both the ends. It is uniformly heated such that the increase in temperature is 30°C. The stress developed in the rod is
A cube having each side of length a, is constrained in all directions and is heated uniformly so that the temperature is raised to T°C. If α is the thermal coefficient of expansion of the cube material and E is the modulus of elasticity, the stress developed in the cube is
A steel rod of length 300 mm is held between two fixed supports so that the rod cannot elongate or contract in the axial direction. If the temperature of the rod is raised by 20°C, the axial stress induced in the rod due to this rise in temperature is
(Take E = 200 GPa, α = 11.5 x 10-6/°C)
|
45 videos|314 tests
|