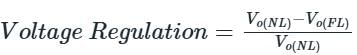Test: Auto-Transformer - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2026 - Test: Auto-Transformer
While comparing potential transformer to an auto transformer, a potential transformer transfers power ________
The statements which support the points that auto transformers are disadvantageous as compared to 2-winding transformer
I. Weight of conductor reduces
II. Direct electrical contacts
III. Leakage reactance reduces
IV. Lower short-circuit current
I. Weight of conductor reduces
II. Direct electrical contacts
III. Leakage reactance reduces
IV. Lower short-circuit current
I. KVA rating : 1/(1-k)
II. Losses : (1-k)
III. Impedance drop = 1/(1-k)
Which of the above are correct for an auto transformer when compared to the identical rating two winding transformer?
II. Losses : (1-k)
III. Impedance drop = 1/(1-k)
Which of the above are correct for an auto transformer when compared to the identical rating two winding transformer?
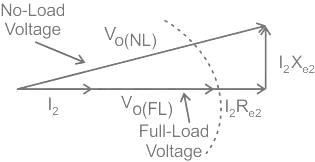
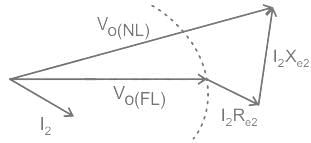
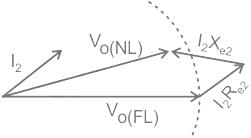
The voltage regulation of a transformer at full-load 0.8 p.f leading is -2%. Its voltage regulation at full load 0.8 p.f lagging
The voltage regulation of a transformer is not dependent on its
Three transformers having identical dimensions but with core of iron, aluminium and wood are wound with same number of turns and have same supply.Then choose the order for hysteresis losses.
Maximum efficiency of a transformer for a constant load current , occurs at
A 1-phase tranformer has a leakage impedance of 1+ j4 Ω for primary and 3+ j11 Ω for secondary windings. This transformer has
Which of the following power factor gives positive voltage regulation in transformer?
|
25 docs|247 tests
|
|
25 docs|247 tests
|