Test: Cathode Ray Oscilloscope - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Cathode Ray Oscilloscope
With _______ testing it is possible to see even smallest distortions clearly on CRO.
Which of the following is used to measure the transmission or reflection of visible light, UV light or infrared light ?
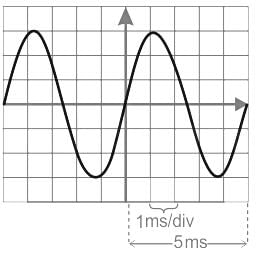
What is the frequency of the sinusoidal signal that occupies five horizontal divisions and three vertical divisions on a CRO for one complete cycle, if the time base is set at 1 ms per division?
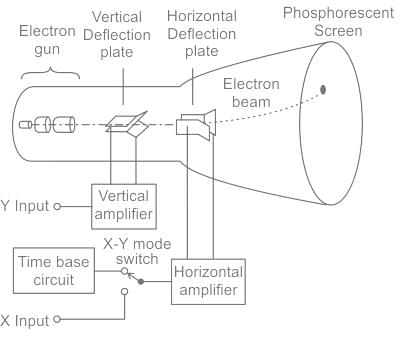
For display of a sine wave in a CRO, what waveform is applied ot the horizontal plates?
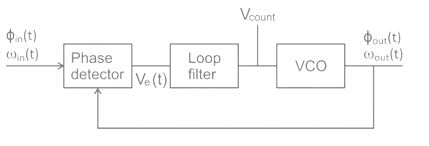
When a PLL is being used as a frequency synthesizer, the output is taken from
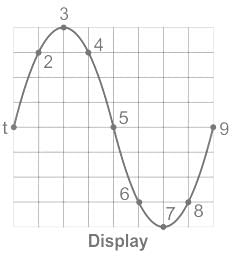
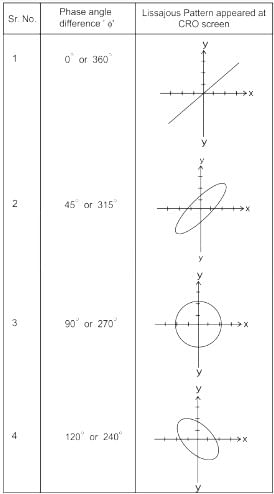
Lissajous pattern obtained on CRO is used to determine
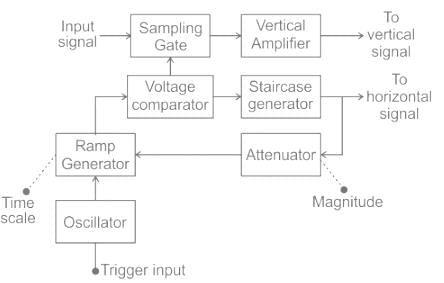
For the recording of very fast random signals, the most suitable instrument would be
Which of the following is used to analyze all kinds of matters?