Test: Graph Theory - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Graph Theory
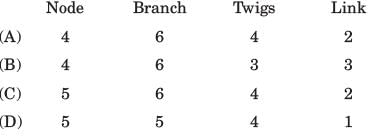
A graph of an electrical network has 4 nodes and 7 branches. The number of links l, with respect to the chosen tree, would be
Branch current and loop current relation are expressed in matrix form as
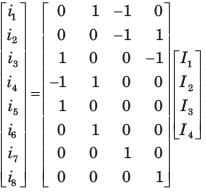
where ij represent branch current and Ik loop current. The number of independent node equation are
If the number of branch in a network is b, the number of nodes is n and the number of dependent loop is l, then the number of independent node equations will be
Branch current and loop current relation are expressed in matrix form as
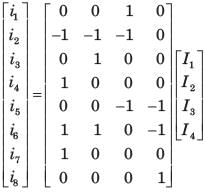
where ij represent branch current and Ik loop current.
Q. The rank of incidence matrix is
Branch current and loop current relation are expressed in matrix form as

where ij represent branch current and Ik loop current.
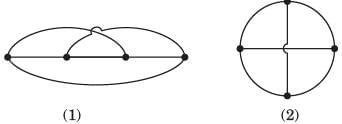
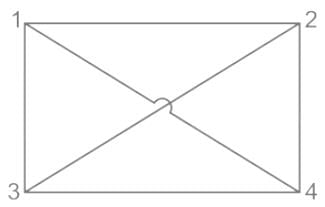
Q. The directed graph will be