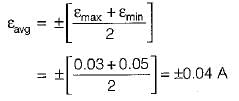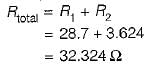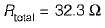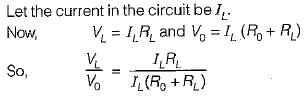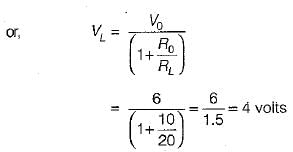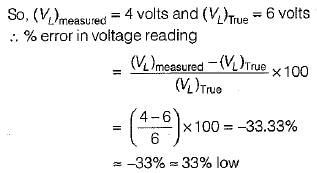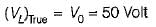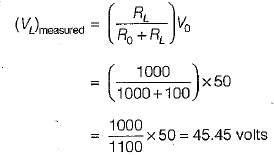Test: Introduction to Electrical & Electronics Measurements - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2026 - Test: Introduction to Electrical & Electronics Measurements
in present day measurement systems
The use of electronic instruments is becoming more extensive because they have
A thermometer is calibrated 150°C to 200°C. The accuracy is specified within ±0.25 percent of instrument span. The maximum static error is
A set of independent current measurements were recorded as 10.03, 10.10, 10.08 and 10.11 A, The average range of error is
Two resistors R1, and R2 are connected in series with R1 = 28.7 Ω and R2 = 3.624 Ω. The total resistance to the appropriate number of significant figures can be written as
A Wheatstone bridge requires a change of 8 a in the unknown arm of the bridge to produce a change in deflection of 3 mm of the galvanometer. The deflection factor (scale factor) is
A moving coil voltmeter has a uniform scale with 100 divisions, the full scale reading is 200 V and 1/10 of a scale division can be estimated with a fair degree of certainty.The resolution of the instrument in volt is
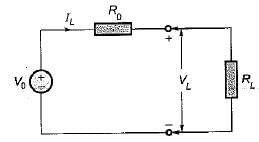
A multimeter having a sensitivity of 2 kΩ/V is used for the measurement of voltage across a circuit having an output resistance of 10 kΩ. The open circuit voltage of the circuit is 6 volts. The percentage error in multimeter reading when it is set to 10 volt is given by
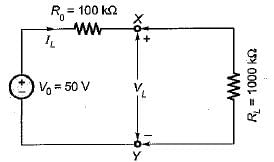
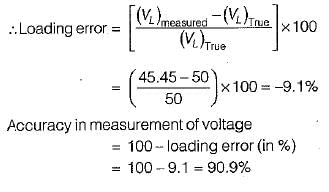
A 50 V range voltmeter is connected across the terminals X and Y of the circuit shown in figure below. The voltage across the terminals are measured both under open circuit and loaded conditions.
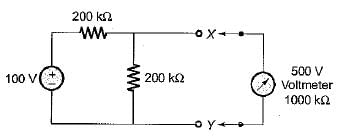
The accuracy in the measurement of voltage across the terminals X and Y in percent is
The number of significant figures in the two resistors having resistances 4 x 106 kΩ and 0.345 kΩ are respectively
|
26 docs|257 tests
|
|
26 docs|257 tests
|