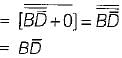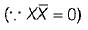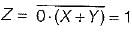Test: Logic Gates & Switching Circuits- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Logic Gates & Switching Circuits- 2
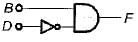
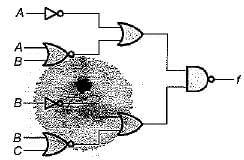
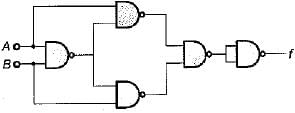
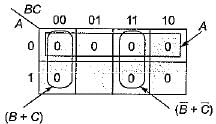
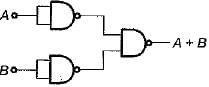
For the logic diagram shown below, the output f is

The minimum number of NOR gates requires to implement the expression
f(A, B, C) = πM(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 7) is
f(A, B, C) = πM(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 7) is
Consider the following statements associated with logic gates:
1. An OR gate in the positive logic system becomes an AND gate in the negative logic system and vice-versa.
2. The dual of an expression is obtained by changing ANDs to ORs, ORs to ANDs.Os to 1s, to Os and by complementing the variables.
3. NAND and NOR are the only two available universal logic gates.
4. Universal gates do not follow commutative law
5. On logic diagrams, an inversion bubble at the point where the input is connected to a gate, indicates an active-HIGH input.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
1. An OR gate in the positive logic system becomes an AND gate in the negative logic system and vice-versa.
2. The dual of an expression is obtained by changing ANDs to ORs, ORs to ANDs.Os to 1s, to Os and by complementing the variables.
3. NAND and NOR are the only two available universal logic gates.
4. Universal gates do not follow commutative law
5. On logic diagrams, an inversion bubble at the point where the input is connected to a gate, indicates an active-HIGH input.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
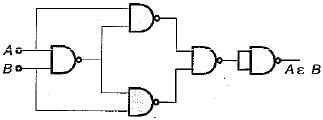
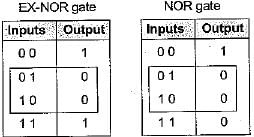
The number of two input NAND gate required to implement an OR gate and an EX-NOR gate are respectively
Three set of simultaneous equations are given by
(i) 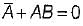
(ii) AB = AC
(iii) 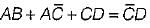
The solution of the above three set of simultaneous equations will be
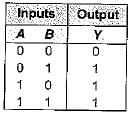
If one of the input to an EX-NOR gate is fixed to logic ‘1’, then output of this gate will be
An XOR gate produces output 1 only when two inputs are
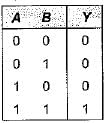
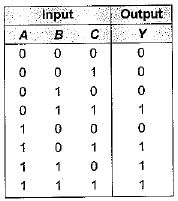
Consider the truth table shown beiow:
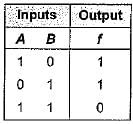
The logic gate represented by the above truth table is
A logic gate is an electronic circuit which
The output of a logic gate is ‘0’ when both its inputs are different. The gate is
For the diode circuit shown below, both the diodes D1, and D2 are ideal.
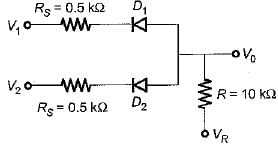
If VR= +5 V, then match List-I (Values of V1 and V2) with List-Il (Output voltage V0) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
V1 = 0 and V2 = 5 volt
V1 = V2 = 5 volt
V1 = V2 = 0 volt
List-ll
1 . 5 volt
2. 0.12 volt
3. 0.24 volt
4. 2.5 volt
Codes:
A B C
(a) 3 1 2
(b) 4 1 3
(c) 2 3 4
(d) 3 4 2
A circuit has three inputs and one output. The output is 1 if at least two of the three input variables are 1, otherwise it is zero. The minimum number of basic gates required to implement the output (Y) are
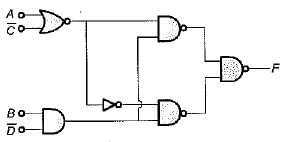
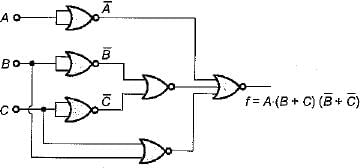
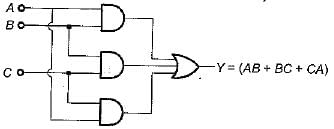
The boolean expression for the output f of the digital circuit shown below is
In the truth table of an N-input OR gate, in the column for the output of the gate,
Consider the following statements associated with logic gates:
1. Logic circuit of any complexity can be realised by using only the three basic gates namely AND, GR and NOT.
2. AND, OR and NOT .gates are called universal building blocks.
3. AND/OR/INVERT logic (AO! logic) can be converted to NAND logic or NOR logic.
4. A NAND gate can be used as an inverter by connecting all its input terminals except one, to logic 1 and applying the signal to be inverted to the remaining terminal.
Q. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Assertion (A): When a number of variables are to be X-NORed, a number of two-input X-NOR gates can be used.
Reason (R): Three or more variable X-NOR gates will make the circuit costly.
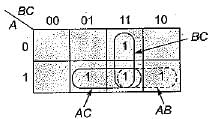
The simplified version of the logic circuit shown below consists of
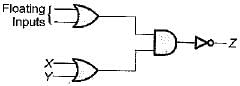
The circuit shown in figure is a ECL OR-AND- INVERTER circuit. The output Z is


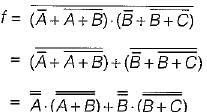
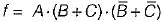


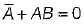
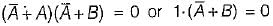
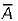 must be 0 and B must be 0 Hence, A = 1 and B = 0
must be 0 and B must be 0 Hence, A = 1 and B = 0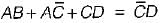

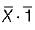 = X = Input
= X = Input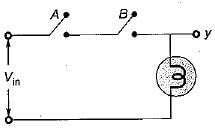
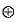 A = 0
A = 0
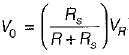
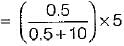
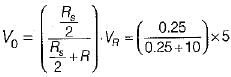
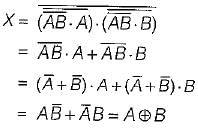
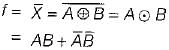
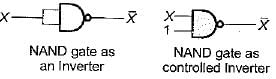
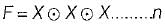 times, then the value of F is
times, then the value of F is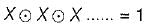
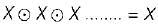
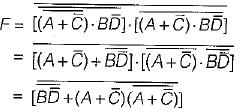 (∴ (X + Y) (X + Z) = X + YZ)
(∴ (X + Y) (X + Z) = X + YZ)