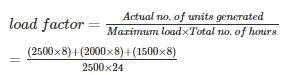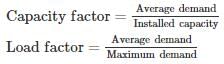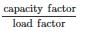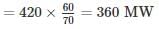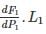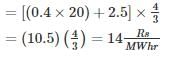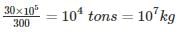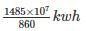Test: Power Systems- 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Power Systems- 1
Which of the following rotor is used in thermal power plants?
Which of the following is not the advantage of higher transmission voltage:
In a hydroelectric plant, the available head is 80 m for a discharge 12m3/sec, and overall efficiency of the PowerStation of 80%. The specific weight of water is 9.81 k/m2. Then the power developed is – (in MW)
Consider a power system with three identical generators. The transmission losses are negligible. One generator(G1) has a speed governor which maintains its speed constant at the rated value, while the other generators (G2 and G3) have governors with a drop of 5%. If the load of the system is increased, then in steady state.
An industrial consumer has a daily load pattern of 2500 kW, 0.8 lag for 8 hours, 2000 kW, 0.6 lag for 8 hours and 1500 kW, unity power factor for 8 hours. What is the load factor?
A generating station has the following data:
Installed capacity = 420 MW; capacity factor = 60%
Annual load factor = 70%.
The minimum reserve capacity of the station is – (in MW)
Determine the incremental cost of received power of the plant shown in the figure below, if the incremental cost of production is 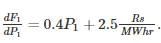 ________
________ 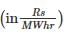
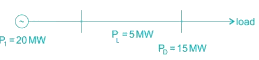
A steam power station spends Rs. 30 lakhs per annum for coal used in the station. The coal has a calorific value of 5000 kcal/kg and costs Rs. 300 per ton. If the station has thermal efficiency of 33% and electrical efficiency of 90%, find the average load on the station. (in kW)
|
25 docs|247 tests
|
|
25 docs|247 tests
|