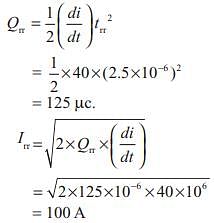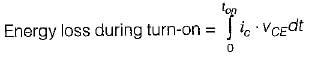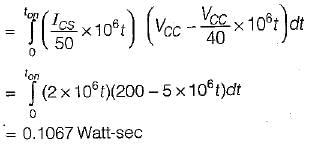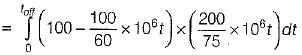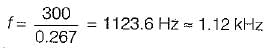Test: Power Semiconductor Diode & Transistors - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Electrical Engineering (EE) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Power Semiconductor Diode & Transistors
In a Schottky diode junction is formed between
Assertion (A) : A Schottky diode has very high reverse voltage rating as compared to alloyed and diffused diodes.
Reason (R) : In a Schottky diode the metallic layer is surrounded by a ring of insulating material such as SiO2.
Reason (R) : In a Schottky diode the metallic layer is surrounded by a ring of insulating material such as SiO2.
Consider the following statements:
1. By increasing the rate of recombination and removal of minority carrier, reverse recovery period can be reduced.
2. In fast recovery diode, rate of recombination is decreased.
3. MOSFET and transistors are used in high power applications.
4. IGBT is having all the good properties of a transistors and MOSFET.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
1. By increasing the rate of recombination and removal of minority carrier, reverse recovery period can be reduced.
2. In fast recovery diode, rate of recombination is decreased.
3. MOSFET and transistors are used in high power applications.
4. IGBT is having all the good properties of a transistors and MOSFET.
A power transistor
1. cannot be easily paralleled.
2. is susceptible to secondary breakdown.
3. has low transconductance than MOSFET.
4. has negative temperature coefficient on collector current.
5. has low switching speed than MOSFET
Which of the above characteristics are possessed by a power transistor?
The rate of fall of diode current for a diode is 40 A/ms and reverse recovery time is 2.5 ms. The Peak reverse current (assuming the softness factor as 0.5) is given by
Which of the following are not a unidirectional current devices?
1. BJT
2. TRIAC
3. SCR
4. GTO
5. IGBT
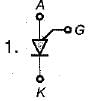
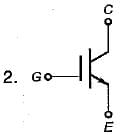
Match List-I (Power devices) with List-Il (Symbols) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. IGBT
B. MCT
C. Programmable Unijunction Transistor (PUT)
D. Silicon Controlled Switch (SCS)
List-II
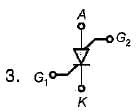
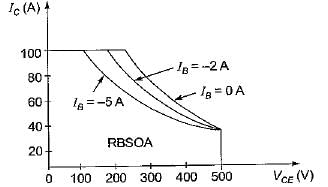
Assertion (A): With increased reverse bias, the reverse blocking safe operating area increases in size.
Reason (R): The reverse blocking safe operating area is a plot of collector current versus collector-emitter voltage.
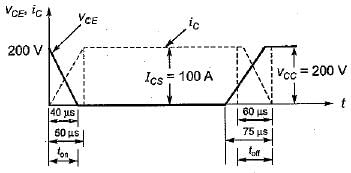
A power transistor has its switching, waveforms as shown in figure. If the average power loss in the transistor is limited to 300 W, the switching frequency at which the transistor can be operated is approximately equal to
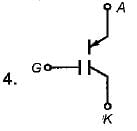
Which one of the following suited for current controlled device
|
25 docs|247 tests
|
|
25 docs|247 tests
|