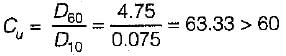Test: Soil Classification & Soil Structure - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2026 Mock Test Series - Test: Soil Classification & Soil Structure
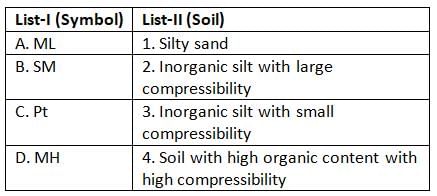
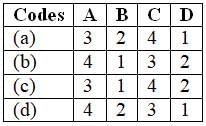
Match List-I (Symbol) with List-ll (Soil) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:


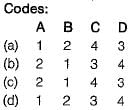
Match List-I (Soil classification symbol) with List-ll (Soil property) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. GW
B. SW
C. ML
D. CL
List-ll
1. Soil having uniformity coefficient > 6
2. Soil having uniformity coefficient > 4
3. Soil have low plasticity
4. Soil have low compressibility
A. GW
B. SW
C. ML
D. CL
1. Soil having uniformity coefficient > 6
2. Soil having uniformity coefficient > 4
3. Soil have low plasticity
4. Soil have low compressibility

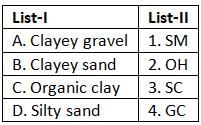
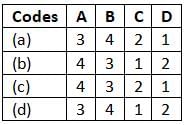
Match List-I (Soils) with List-II (Group symbols) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:


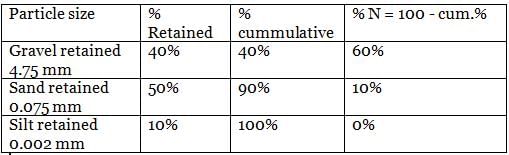
A soil mass contains 40% gravel, 50% sand and 10% silt. This soil can be classified as
Inorganic soil with low compressibility are represented by
Sieve analysis on a dry soil sample of mass 1000g showed that 980g and 270g of soil pass through 4.75 mm and 0.075 mm sieve respectively. The liquid limit and plastic limit of the soil fraction passing through 425 μ sieves are 40% and 18%, respectively. The soil may be classified as
In a particular soil sample, laboratory analysis has yielded the following result:
1. Sand - 20%
2. Silt - 30%
3. Clay - 50%
Without using the textural chart, the correct textural classification of the soil would be
The description of ‘sandy silty clay’ signifies that
Sieve analysis on a dry soil sample of mass 1000 g showed that 980 g and 270 g of soil pass through 4.75 mm and 0.075 mm sieve, respectively. The liquid limit and plastic limits of the soil fraction passing through 425 m sieves are 40% and 18%, respectively. The soil may be classified as
Consider the following statements:
1. Coarse-grained soil having fines (<75μ in size) between 5% and 12%, have a dual symbol according to IS code for soil classification
2, At liquid limit, all soils have the same shearing strength.
3. Lower the shrinkage limit, greater is the volume change in a soil with change in water content.
Of these statements:
|
33 docs|291 tests
|