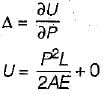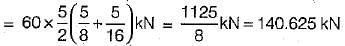Test: ILD & Rolling Loads - 3 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topicwise Question Bank for Civil Engineering - Test: ILD & Rolling Loads - 3
For the pin-joined plane truss shown in the below figure, which of the following diagrams represents the influence line for the bar force in the member CH?
+ sign indicates tension
- sign indicates compression

+ sign indicates tension
- sign indicates compression
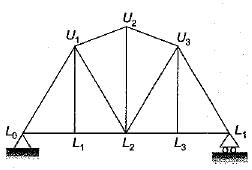
Which one of the following is the influence line for the force in the member U1L2 of the plane pin-jointed frame shown in the figure given below?

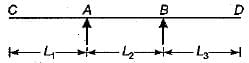
Which one of the following is the influence line for reaction at A of the beam shown in the figure?

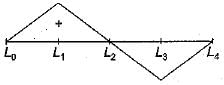
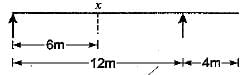
Select the correct influence line diagram for shear force at x of the following beam
The maximum bending moment at the left quarter point of a simple beam due to crossing of UDL of length shorter than the span in the direction left to right, would occur after the load had just crossed the section by
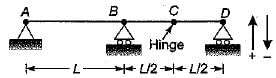
For the continuous beam shown in figure, the influence line diagram for support reaction at D is best represented as
Consider the following statements:
1. Influence Line Diagram (ILD) for SF at the fixed end of a cantilever and SFD due to unit load at the free end are same.
2. ILD for BM at the fixed end of a cantilever and BMD due to unit load at the free end are same.
Which of these statements is/are correct?
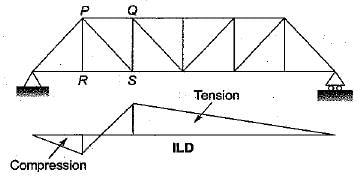
The influence line diagram (ILD) shown is for the member
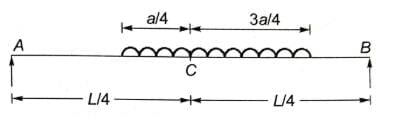
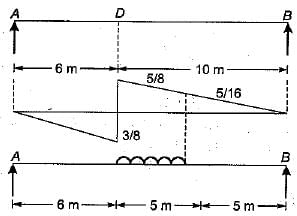
A uniformly distributed line load of 60 kN per metre run of length 5 meters on a girder of span 16 metres. What is the maximum positive shear force at a section 6 metres from the left end.
The wheel loads 200 kN and 80 kN spaced 2 m apart move on the span of girder of span 16 metres. What is the maximum bending moment that will occur at a section 6 metres from the left end.