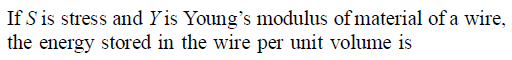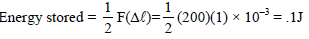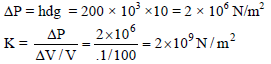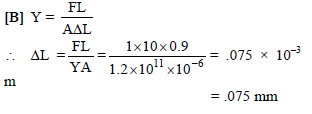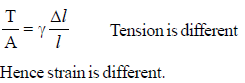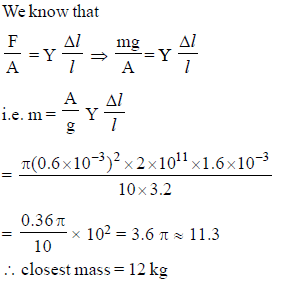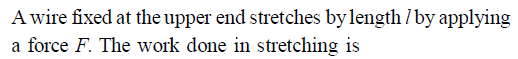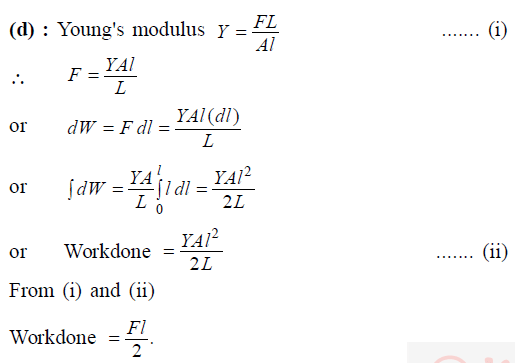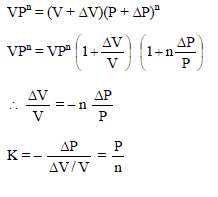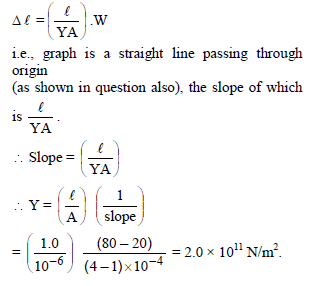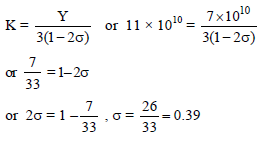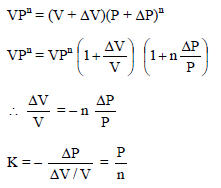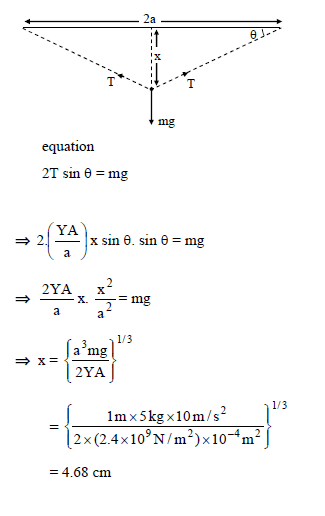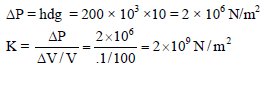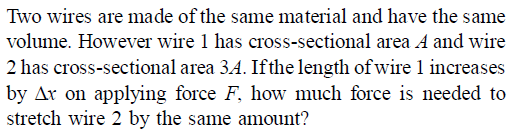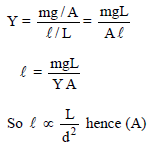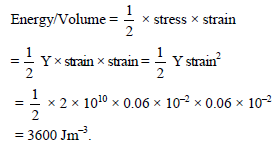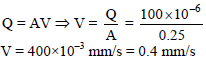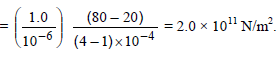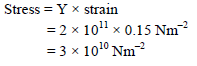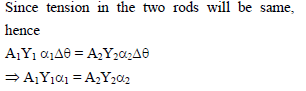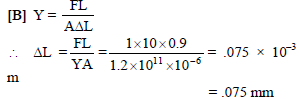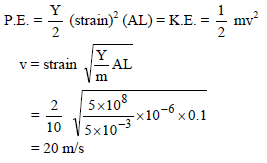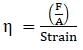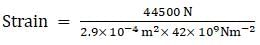Chapter Test: Elasticity (Mechanical Properties of Solids) - 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chapter Test: Elasticity (Mechanical Properties of Solids) - 1
A wire suspended vertically from one of its ends is stretched by attaching a weight of 200 N to the lower end. The weight stretches the wire by 1mm. Then the elastic energy stored in the wire-
A ball falling in a lake of 200 m shows a decrease of 0.1% in its volume. The Bulk modulus of elasticity of the material of the ball is -(take g =10 m/s2)
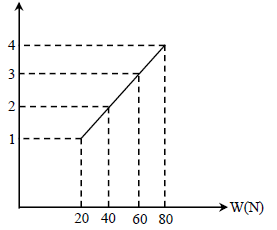
A copper wire of length 0.9 m and crosssectional area 1.0 mm2 is stretched by a load of 1kg. Young's modulus for copper is 1.2 × 1011 N/m2 and g = 10m/s2. The extension in wire in mm is -
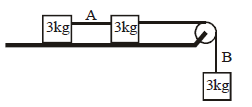
Three equal masses of 3 kg are connected by two massless strings of cross sectional area 0.005 cm2 and Young modulus is 2 × 1011 N/m2 each.The longitudinal strain in the wires
A steel wire, 3.2 m long, has a diameter of 1.2 mm. The wire stretches by 1.6 mm when it bears a load. Young's modulus for steel is 2.0 × 1011 Pa. The mass of the load is closest to:
A gas undergoes a process in which the pressure and volume are related by VPn = constant. The bulk modulus of the gas is –
Given the following values for an elastic material: Young's modulus = 7 × 1010 Nm–2 and Bulk modulus = 11 × 1010 Nm–2 . The Poisson's ratio of the material is -
A gas undergoes a process in which the pressure and volume are related by VPn = constant. The bulk modulus of the gas is –
A wire of length '2m' is clamped horizontally between two fixed support. A mass m = 5 kg is hanged from middle of wire. The vertical depression in wire in equilibrium is (young modulus of wire = 2.4 × 109 N/m2, crosssectional area = 1 cm2) -
A ball falling in a lake of 200 m shows a decrease of 0.1% in its volume. The Bulk modulus of elasticity of the material of the ball is -
(take g =10 m/s2)
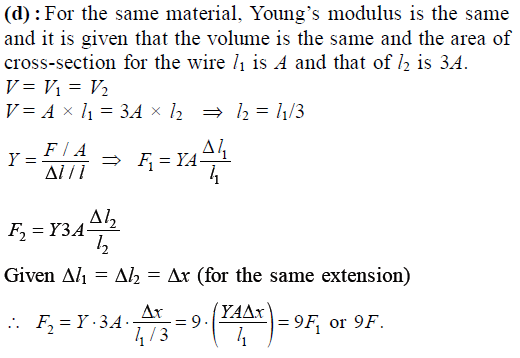
The following four wires are made of the same material. Which of these will have the largest extension when the same tension is applied -
A metal rod of Young's modulus 2 × 1010 Nm–2 undergoes an elastic strain of 0.06%. The enrgy per unit volume stored in Jm–3 is -
n steel, the young's modulus and the strain at the breaking point are 2 × 1011 Nm–2 and 0.15 respectively. The stress at the break point for steel is –
Blood is flowing at the rate of 100 cm3/s in a capillary of cross sectional area 0.25m2. The velocity of flow is -
In steel the Young's modulus and the strain at the breaking point are 2 × 1011 Nm–2 and 0.15 respectively. The stress at the break point for steel is-
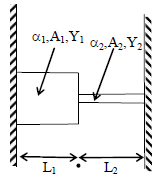
Two elastic rods are joined between fixed supports as shown in the figure. Condition for no change in the lengths of individual rods with the increase of temperature is –
(α1,β2 = linear expansion coefficient, A1, A2 = Area of rods, Y1,Y2 = young modulus )
A copper wire of length 0.9 m and crosssectional area 1.0 mm2 is stretched by a load of 1kg. Young's modulus for copper is 1.2 × 1011
N/m2 and g = 10m/s2. The extension in wire in mm is -
The rubber cord catapult has a cross-section area 1 mm2 and total unstretched length 10 cm. It is stretched to 12 cm and then released to project a stone of mass 5 gm. Taking Young’s modulus Y of rubber as 5 × 108 N/m2, the velocity of projection will be -
A steel rod 2.0 m long has a cross-sectional area of 0.30 cm2 . It is hung by one end from a support, and a 550-kg milling machine is hung from its other end. Determine the resulting strain. Young's Modulus of Steel (Y) = 20×1010 Pa
A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm × 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain? Take Young's modulus of copper as 42 × 109Pa
What diameter should a 10-m-long steel wire have if we do not want it to stretch more than 0.5 cm under a tension of 940 N? Take Young's modulus of steel as 20 × 1010 Pa
Elasticity is the property of a body, by virtue of which
Elastomers are materials