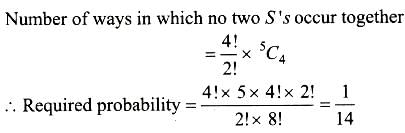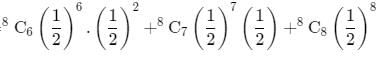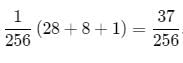Test: Probability- 1 - Commerce MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Mathematics (Maths) Class 11 - Test: Probability- 1
Probability of getting a number between 1 and 100, which is divisible by 1 and itself only, is
Two players toss four coins each. The probability that both obtain the same number of heads is
If three dice are thrown, then the probability that they show the numbers in A.P. is
A cubical dice has 3 on three faces, 2 on two faces and 1 on the 6 thth face .It is tossed twice. The chance that both the tosses show an even number is
A coin is tossed once. If a head comes up, then it is tossed again and if a tail comes up, a dice is thrown. The number of points in the sample space of experiment is
A drawer contains 5 black socks and 4 blue socks well mixed. A person searches the drawer and pulls out 2 socks at random. The probability that they match is
A bag contains 5 white, 7 red and 4 black balls. Four balls are drawn one by one with replacement. The chance that atleast two balls are black is
A and B take turn in throwing a pair of dice. A wins if he throws a total of 5 before B throws a total of 7. If A has the first throw, the probability of his winning the game is
A determinant is chosen at random from the set of all determinants of order 2 with elements 0 or 1 only. The probability that the value of the determinant chosen is positive is
If the letters of the word ‘ INDEPENDENCE ‘ are written down at random in a row, then the chance that no two E’s occur together is
The letters of the word ‘ASSASSIN ‘ are written at random in a row. The chance that all the similar letters occur together is
A person throws successively with a pair of dice. The chance that he throws 9 before he throws 7 is
Let A be set of 4 elements. From the set of all functions from A to A, a function is chosen at random. The chance that the selected function is an onto function is
Both A and B throw a dice. The chance that B throws a number higher than that thrown by A is
Both A and B throw a dice. The chance that B throws a number not less than that thrown by A is
Two dice are thrown. The number of sample points in the sample space when 6 does not appear on either dice is
8 coins are tossed at a time. The probability of getting 6 heads up is
A dice is rolled 6 times. The probability of obtaining 2 and 4 exactly three times each is
A dice has 3 faces each bearing ‘ 2 ‘ and three faces each bearing ‘ 6 ‘. It is rolled once. The probability of showing up ‘a six ‘ is
Neelam and Nidhi throw with a dice. The chance that both Neelam and Nidhi throw the same number is
A dice is tossed once and even number has come up. The chance that it is either 2 or 4 is
What is the probability of getting a sum of eight if two dice are thrown at once?
The probability of having atleast one head in 5 throws of a coin is
A fair coin is tossed a fixed number of times. If the probability of getting 4 heads is equal to the probability of getting 7 heads, then the probability of getting 2 heads is
|
75 videos|238 docs|91 tests
|