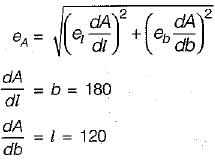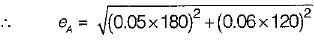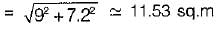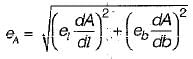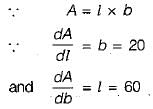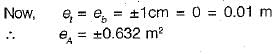Test: Fundamental Concepts, Accuracy & Errors - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Fundamental Concepts, Accuracy & Errors - 1
Surveys which are carried out to depict mountains, rivers, water bodies, wooded areas and other cultural details, are known as
The sides of a rectangle are (120 ± 0.05)m and (180 ± 0.06) m. The probable error in the area will be
Which of the following scales is largest one?
The principle of ‘working from whole to part’ is used in surveying because
Which one of the following surveys is employed for collecting sufficient data in connection with sewage disposal and water supply works?
Theory of errors and adjustments deals with minimizing the effects of
A plot of land 60 m x 20 m is measured by a steel tape. If the standard error of length and width measurements is taken as ±1 cm, then the standard error of the area of the plot would be
Which one of the following closely represent the shape of the earth?
The representative fraction 1/2500 means that the scale 1 cm is equal to