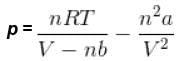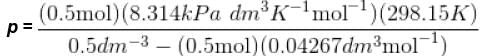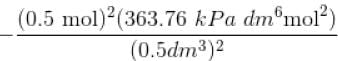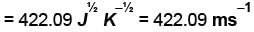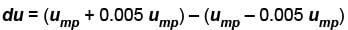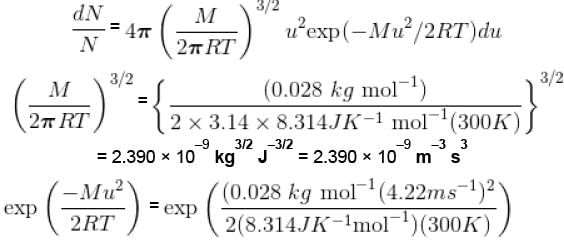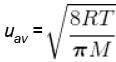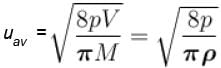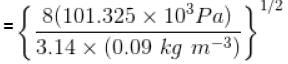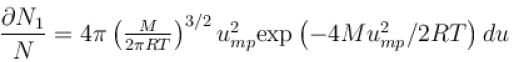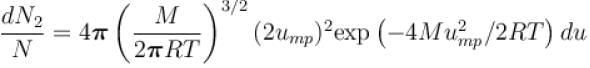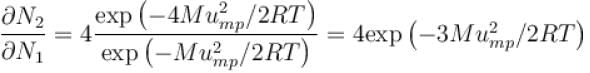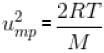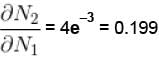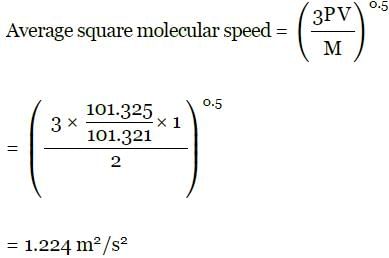Kinetic Theory Of Gases MCQ Level – 2 (part - 1) - IIT JAM MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Kinetic Theory Of Gases MCQ Level – 2 (part - 1)
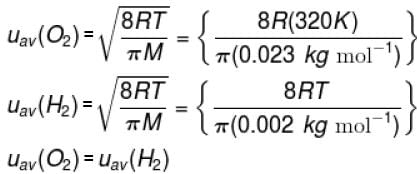
The temperature at which the average speed of H2 equals that of O2 at 320K.
Select one:
Select one:
The critical constant for water are 647 K, 22.09 MPa and 0.0566 dm3 mol-1, the value of a and b are respectively.
Select one:
Select one:
Calculate molecular diameter d of helium from its van der Waals constant b = 24 cm3 mol-1
Select one:
Select one:
The kinetic energy of 0.5 mol of an ideal gas at 273 K
Select one:
The mean free path of the molecule of a certain gas at 300K is 2.6×10-5m. The collision diameter of the molecule is 0.26 nm then the number of molecule per unit volume of the gas.
Select one:
Using vander Waals equation, the pressure exerted by 22g of carbon dioxide in 0.5 dm3 at 298.15 K is (Given : a = 363.76 kPa dm6 mol-2 and b = 42.67 cm3 mol-1 )
Select one:
Calculate the fraction of N2 molecule at 101.325 kPa and 300 K whose speed are in the range of 
Select one:
The average speed of H2 molecules, if the density of the gas at 101.325 kPa is 0.09gdm-3
Select one:
What is the ratio of the number of molecule having speed in the range of 2ump and 2ump + du to the number of molecule having speeds in the range of ump + du.
Select one:
A bulb of capacity 1 dm3 contain 1.03 × 1023 gaseous hydrogen molecules and the pressure exerted by these molecules is 101.325 kPa. Calculate the average square molecular speed.
Select one:


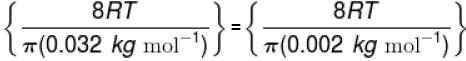

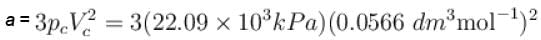

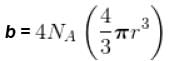
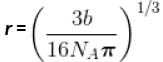
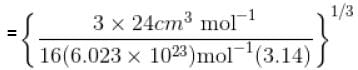
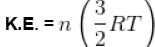
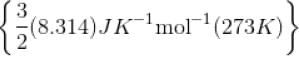
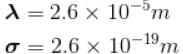
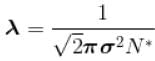
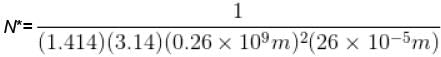
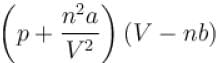 = nRT
= nRT