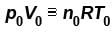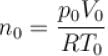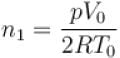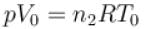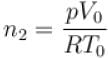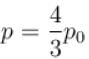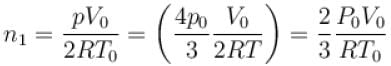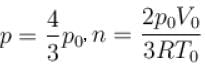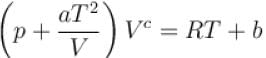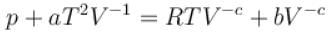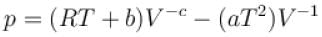Kinetic Theory Of Gases MSQ - IIT JAM MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Kinetic Theory Of Gases MSQ
A gas in container A is in thermal equilibrium with another gas in container B, both contain equal masses of two gases in the respective containers which of the following can be true?
Select one or more:
Select one or more:
Let 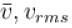 and vmp respectively denote mean speed, root mean square speed and most probable speed of the molecules in an ideal monoatomic gas at absolute temperature T. The mass of molecule is m. Then,
and vmp respectively denote mean speed, root mean square speed and most probable speed of the molecules in an ideal monoatomic gas at absolute temperature T. The mass of molecule is m. Then,
Select one or more:
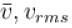 and vmp respectively denote mean speed, root mean square speed and most probable speed of the molecules in an ideal monoatomic gas at absolute temperature T. The mass of molecule is m. Then,
and vmp respectively denote mean speed, root mean square speed and most probable speed of the molecules in an ideal monoatomic gas at absolute temperature T. The mass of molecule is m. Then,Select one or more:
Under which of the following conditions is the law pV = RT obeyed most closely by a real gas
Select one or more:
Select one or more:
A gas mixture consists of molecules of type 1, 2 and 3 with molar masses m1 > m2 > m3 . vrms and 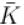 are the rms speed and average kinetic energy of the gases. Which of the following are true?
are the rms speed and average kinetic energy of the gases. Which of the following are true?
Select one or more:
Which of the following statements are true with regards to mean free path?
Select one or more:
The mean free path of a gas molecule is λ1 at temperature T. The pressure and temperature, of both the gas, are made two times their original value. The new mean free path was found to be λ2. Then λ1:λ2 is -
The value of CP – CV = R for a gas in state A and CP – CV = 1.06R in another state B. If pA and pB denote the pressure and TA and TB denote the temperature in the two state, then
Select one or more:
Two identical containers each of volume V0 are joined by a small pipe. The containers contains identical gases at temperature T0 and pressure p0 . One container is heated to temperature 2T0 while maintaining the other at same temperature. The common pressure of gas is p and n is the number of the moles of gas in container at temperature 2T0 .
Select one or more:
The equation of state of a gas is given by 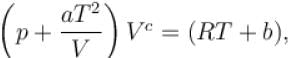 where a, b, c, and R are constants. The isotherms can be represented by p = AVm – BVn where A and B depends only on temperature then.
where a, b, c, and R are constants. The isotherms can be represented by p = AVm – BVn where A and B depends only on temperature then.
Select one or more:
Which of the following is/are false?
Select one or more:


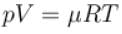
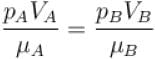
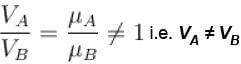
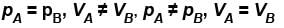
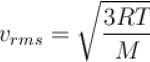
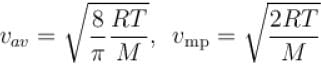
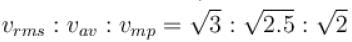
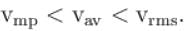

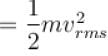
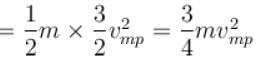
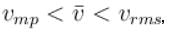 The average kinetic energy of a molecule is
The average kinetic energy of a molecule is 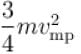

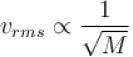 but kinetic energy does not depend on it.
but kinetic energy does not depend on it.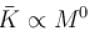
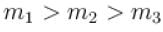
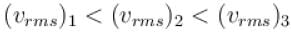
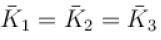
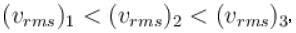
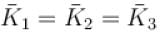
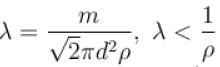 i.e. mean free path is inversely proportional to density of a gas. As
i.e. mean free path is inversely proportional to density of a gas. As 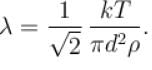
 at constant pressure and
at constant pressure and 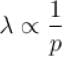 at constant temperature.
at constant temperature.