BPSC (Bihar) Exam > BPSC (Bihar) Tests > BPSC Practice Test- 2 - BPSC (Bihar) MCQ
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - BPSC (Bihar) MCQ
Test Description
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC Practice Test- 2
BPSC Practice Test- 2 for BPSC (Bihar) 2025 is part of BPSC (Bihar) preparation. The BPSC Practice Test- 2 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus.The BPSC Practice Test- 2 MCQs are made for BPSC (Bihar) 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for BPSC Practice Test- 2 below.
Solutions of BPSC Practice Test- 2 questions in English are available as part of our course for BPSC (Bihar) & BPSC Practice Test- 2 solutions in
Hindi for BPSC (Bihar) course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt BPSC Practice Test- 2 | 150 questions in 150 minutes | Mock test for BPSC (Bihar) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for BPSC (Bihar) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 1
Rust is the result of oxidation reaction when the iron (Fe) particles have been exposed to oxygen and moisture. It is chemically known as
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 1
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 2
Which of the following sectors is emphasized at Bihar Business Connect 2024 to diversify the state’s economy?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 2
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 3
Consider the following statements about the Bihar Prohibition and Excise Act, 2016:
1. It prescribes severe penalties for producing illicit liquor.
2. It has completely eradicated the illegal liquor trade in Bihar.
3. It was implemented to address public health issues caused by alcohol.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 3
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 4
What is the mascot “Gudiya” for the Women’s Asian Champions Trophy 2024 inspired by?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 4
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 5
Which of the following is NOT a component of MGNREGA’s key features?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 5
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 6
Which state-level board is responsible for registering temples and trusts in Bihar?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 6
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 7
What is the primary function of gymnemic acid found in Gurmar?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 7
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 8
Consider the following statements regarding the RTI Act, 2005 and the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013:
The RTI Act empowers citizens to request any type of information from private companies responsible for NFSA implementation.
Transparency and accountability in NFSA implementation are ensured through public access to food grain distribution data.
RTI facilitates grievance redressal for beneficiaries facing discrepancies in accessing food grains.
Which of the above statements are correct?
The RTI Act empowers citizens to request any type of information from private companies responsible for NFSA implementation.
Transparency and accountability in NFSA implementation are ensured through public access to food grain distribution data.
RTI facilitates grievance redressal for beneficiaries facing discrepancies in accessing food grains.
Which of the above statements are correct?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 8
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 9
Which bird species is notable in Bihar’s Nagi and Nakti sanctuaries?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 9
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 10
The Viraat Ramayan Mandir is inspired by which of the following architectural sites?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 10
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 11
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 12
Which organization supported Bihar in exporting mangoes internationally?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 12
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 13
The Montreux Record is associated with which of the following?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 13
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 14
What is the primary reason for NABARD’s 21% increase in financial assistance to Bihar?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 14
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 15
What significant milestone has ONGC achieved in the Ganga basin exploration?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 15
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 16
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 17
What is the fixed Minimum Support Price (MSP) for wheat for the 2024-25 season?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 17
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 18
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 19
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 20
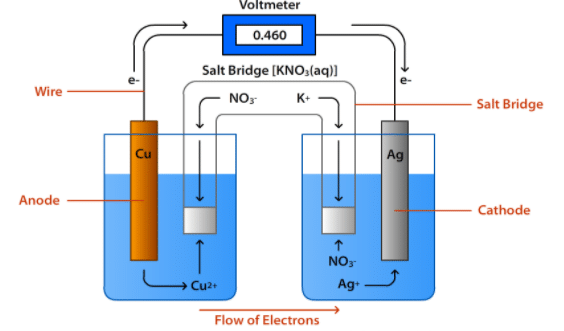
Which of the following cell is used in automobiles and invertors?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 20
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 21
The accidental touch of Nettle leaves creates a burning sensation, which is due to inject of
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 21
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 22
Which one of the following gives the highest amount of hydrogen ions(H+)?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 22
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 23
The intensity of light produced by an unknown source in terms of a standard source is measured by which instrument?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 23
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 24
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 25
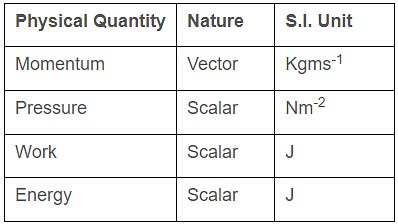
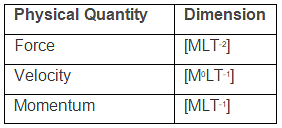
Which of the following is a dimensionless physical quantity?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 25
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 26
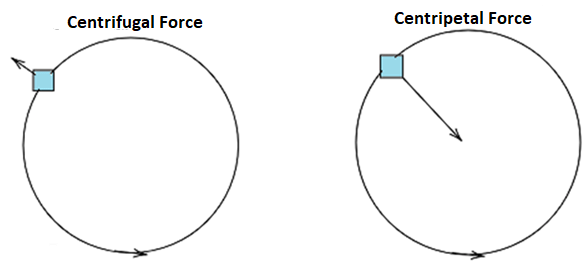
Which of the following forces is responsible for separation of cream from milk in a cream separator?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 26
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 27
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 28
BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 29
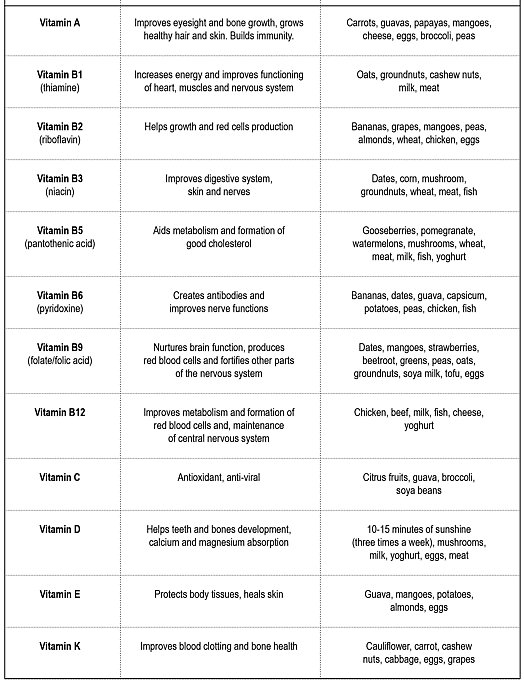
Liver damage is caused due to the overdose of which vitamin?
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 29
Detailed Solution for BPSC Practice Test- 2 - Question 30
View more questions
Information about BPSC Practice Test- 2 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for BPSC Practice Test- 2 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for BPSC Practice Test- 2, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF