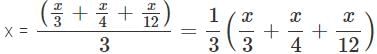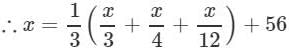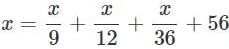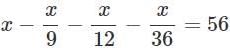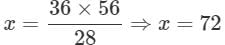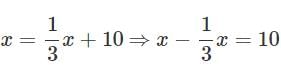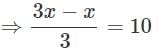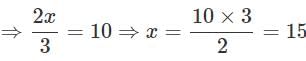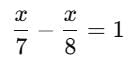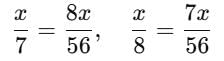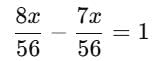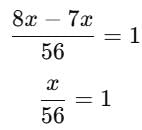Olympiad Test: Linear Equations - Class 8 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Mathematics (Maths) Class 8 - Olympiad Test: Linear Equations
David cuts a loaf of bread into two equal halves and cuts one half into smaller pieces of equal size. Each of the small pieces weighs twenty grams. If he has seven pieces of bread in total, what is the weight of the original loaf?
In the following number sequence, how many such even numbers are there which are exactly divisible by its immediate preceding number but not exactly divisible by its immediate following number?
3 8 4 1 5 7 2 8 3 4 8 9 3 9 4 2 1 5 8 2
3 8 4 1 5 7 2 8 3 4 8 9 3 9 4 2 1 5 8 2
Mary was counting down from 34 and Thomas was counting upwards simultaneously, the number starting from 1 and he was calling out only the odd numbers. Which common number will they call out at the same time if they were calling out at the same speed?
Which of the following is not a linear equation in one variable?
The distance between two mile stones is 230 km and two cars start simultaneously from the milestones in opposite directions and the distance between them after three hours is 20 km. If the speed of one car is less than that of other by 10 km/h, find the speed of each car.
A store has provision which would last for a certain number of men for 21 days. For one seventh of the men it will last for how many days?
An MNC company employed 25 men to do the official work in 32 days. After 16 days, it employed 5 more men and work was finished one day earlier. If it had not employed additional men, it would have been behind by how many days?
A number is 56 greater than the average of its third, quarter and one-twelfth. Find the number.
If 1/3 of a number is 10 less than the original number, then the number is_____.
Solve for x:
6(3x + 2) − 5(6x − 1) = 6(x − 3) − 5(7x − 6) + 12x
The number 299 is divided into two parts in the ratio 5 : 8. The product of the numbers is_____.
If (2/3)rd of a number is 20 less than the original number, then the number is_____.
A number whose seventh part exceeds its eighth part by 1, is _____.
A number consists of two digits whose sum is 9. If 27 is subtracted from the original number, its digits are interchanged. Then the original number is _____.
|
81 videos|415 docs|31 tests
|



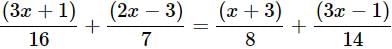
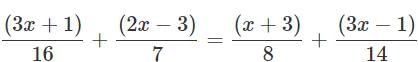
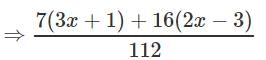
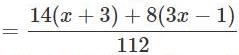

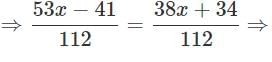 553x − 41 = 38x + 34
553x − 41 = 38x + 34