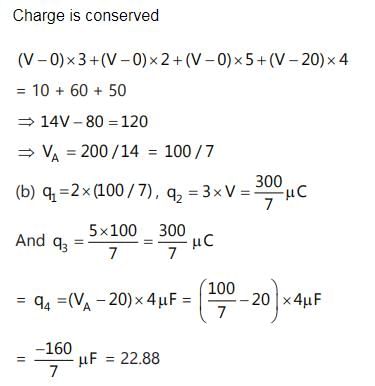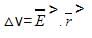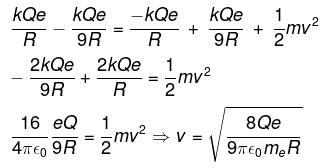DC Pandey Test: Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance - JEE MCQ
18 Questions MCQ Test Physics for JEE Main & Advanced - DC Pandey Test: Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance
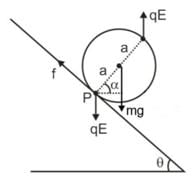
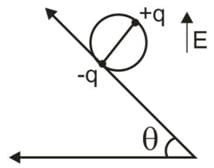
A wheel having mass m has charges +q and -q on diametrically opposite points. It remains in equilibrium on a rough inclined plane in the presence of a uniform vertical electric field E. The value of E is

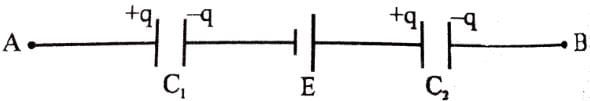
The two plates X and Y of a parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C are given a charge of amount Q each. X is now joined to the positive terminal and Y to the negative terminal of a cell of emf E = Q/C.
Two capacitors of capacitances 1mF and 3mF are charged to the same voltages 5V. They are connected in parallel with oppositely charged plates connected together. Then
Each plate of a parallel plate capacitor has a charge q on it. The capacitor is now connected to a battery. Now,
When a parallel plates capacitor is connected to a source of constant potential difference,
When two identical capacitors are charged individually to different potentials and connected parallel to each other, after disconnecting them from the source :
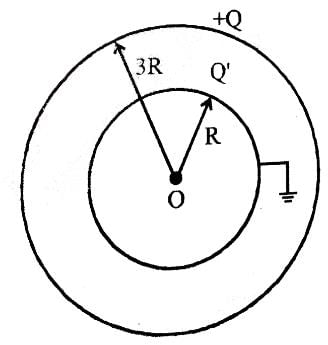
Two thin conducting shells of radii R and 3R are shown in the figure. The outer shell carries a charge +Q and the inner shell is neutral. The inner shell is earthed with the help of a switch S.
Two capacitors of 2mF and 3mF are charged to 150 volt and 120 volt respectively. The plates of capacitor are connected as shown in the figure. A discharged capacitor of capacity 1.5 mF falls to the free ends of the wire. Then
In the circuit shown initially C1, C2 are uncharged. After closing the switch
A circuit shown in the figure consists of a battery of emf 10V and two capacitance C1 and C2 of capacitances 1.0mF and 2.0mF respectively. The potential difference VA – VB is 5V
Two capacitors of equal capacitance (C1 = C2) are shown in the figure. Initially, while the switch S is open, one of the capacitors is uncharged and the other carries charge Q0. The energy stored in the charged capacitor is U0. Sometimes after the switch is colsed, the capacitors C1 and C2 carry charges Q1 and Q2, respectively, the voltages across the capacitors are V1 and V2, and the energies stored in the capacitors are U1 and U2. Which of the following statements is INCORRECT ?
Identify the correct statements.
A solid conducting sphere of radius 10 cm is enclosed by a thin metallic shell of radius 20 cm. A charge q = 20 mC is given to the inner sphere. Find the heat generated in the process, the inner sphere is connected to the shell by a conducting wire -
The plates of a parallel plate capacitor are given charges +4Q and _2Q. The capacitor is then connected across an uncharged capacitor of same capacitance as first one (= C). Find the final potential difference between the plates of the first capacitor.
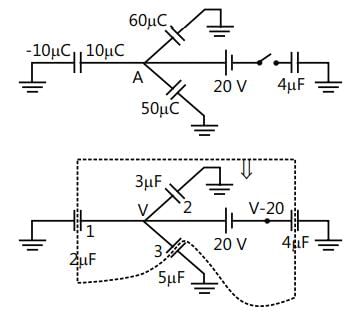
Three capacitors of 2 µF, 3 µF and 5 µF are independently charged with batteries of emf’s 5V, 20V and 10V respectively. After disconnecting from the voltage source. These capacitors are connected as shown in figure with their positive polarity plates connected to A and negative polarity is earthed. Now a battery of 20V and an uncharged capacitor of 4 µF capacitance are connected to the junction A as shown with a switch S. when switch is closed, find:
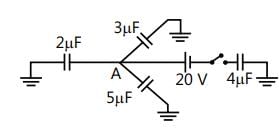
(a) The potential of the junction A.
(b) Final charge on all four capacitros.
Positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to
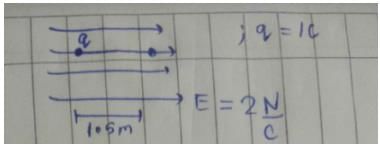
A charge q = 1.0 C moves distance of 1.5 m in the direction of a uniform electric field E of magnitude 2.0 N/C. Find its change in electrostatic potential energy.
Two uniformly charged nonconducting spheres, each of radius R, are fixed in a gravity free space as shown in the figure. If an electron is released at rest from the point A, then its speed just before striking the other sphere is [mass of electron - me]
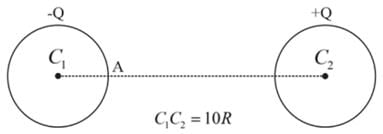
|
289 videos|635 docs|184 tests
|