NEET Exam > NEET Tests > Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - NEET MCQ
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - NEET MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Structural Organisation in Animals
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Test: Structural Organisation in Animals questions and answers have been prepared
according to the NEET exam syllabus.The Test: Structural Organisation in Animals MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals below.
Solutions of Test: Structural Organisation in Animals questions in English are available as part of our course for NEET & Test: Structural Organisation in Animals solutions in
Hindi for NEET course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Structural Organisation in Animals | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for NEET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for NEET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 1
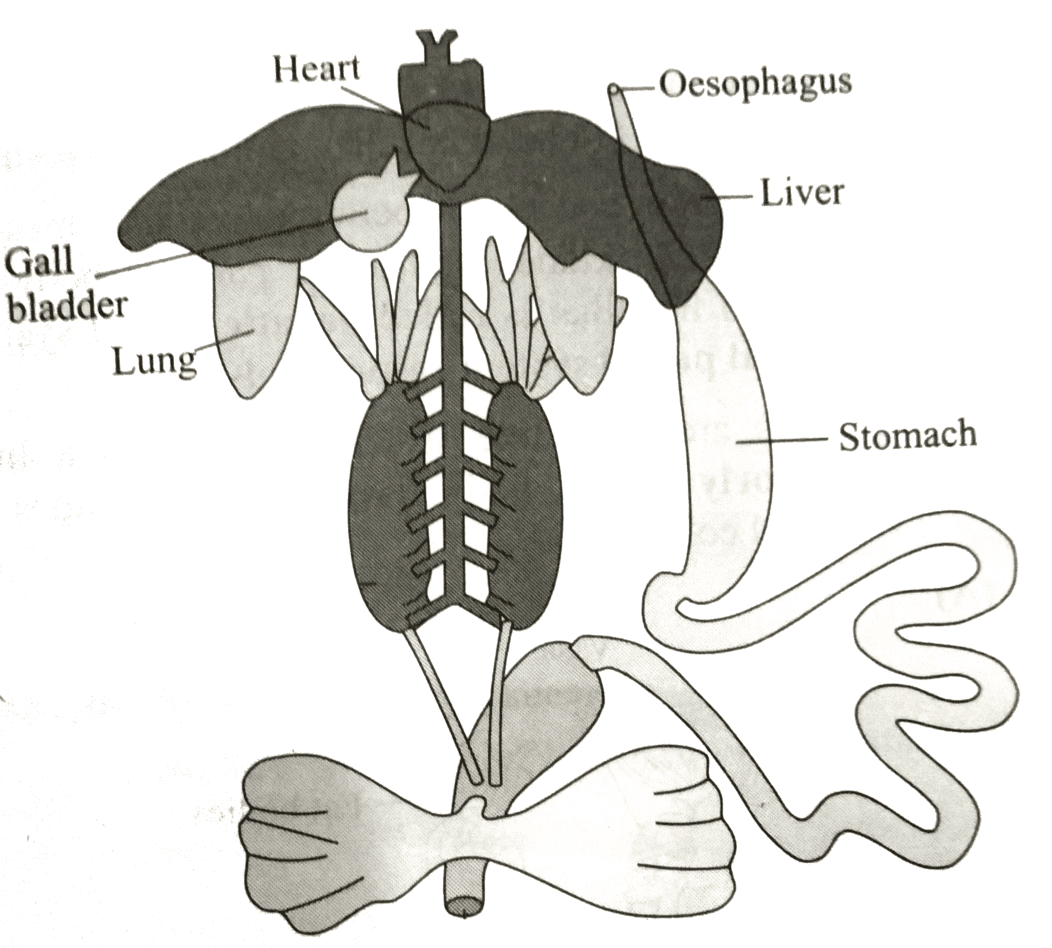
Recognise the figure and find out the correct match.
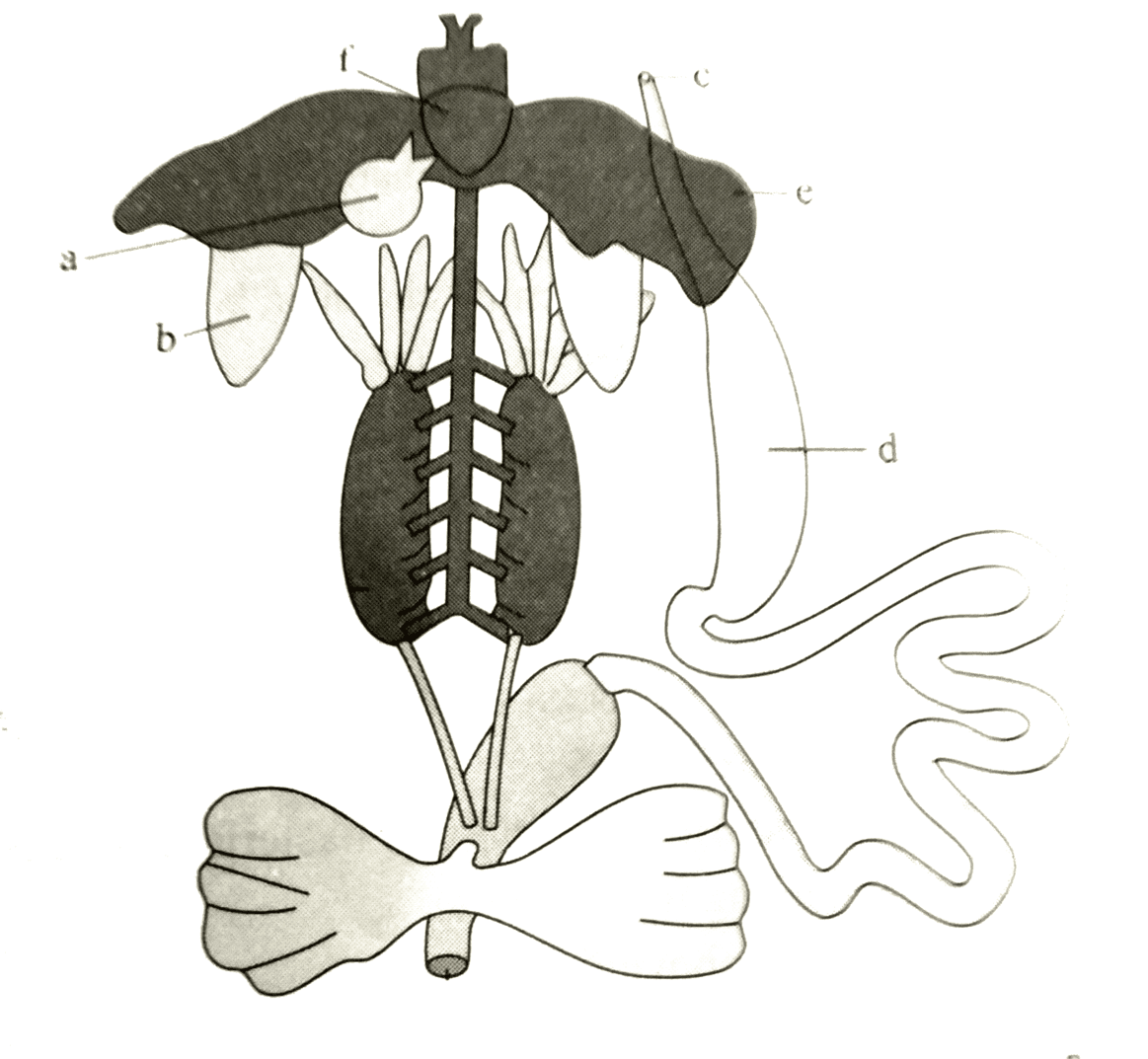

Detailed Solution for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 1
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 2
Assertion (A): Frogs are poikilothermic animals.
Reason (R): They maintain a constant body temperature irrespective of the environment.
Detailed Solution for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 2
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 3
Consider the following statements:
a) Frog’s RBCs are nucleated.
b) Frogs respire only through lungs.
c) Sinus venosus joins the right atrium in frog’s heart.
d) Male frog has vocal sacs.
Choose the correct option:
Detailed Solution for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 3
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 4
Which of the following statements are true for frog’s excretory system?
a) Kidneys are dark red, bean-shaped, located on either side of vertebral column.
b) Excretory waste is ammonia.
c) Ureters in male frogs act as urinogenital ducts.
d) Cloaca is a common chamber for excretion and reproduction.
a) Kidneys are dark red, bean-shaped, located on either side of vertebral column.
b) Excretory waste is ammonia.
c) Ureters in male frogs act as urinogenital ducts.
d) Cloaca is a common chamber for excretion and reproduction.
Detailed Solution for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 4
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 5
Identify correct statements about frog’s reproductive system:
a) Fertilisation is external.
b) A female lays 250–300 ova at a time.
c) Tadpole stage is present in life cycle.
d) Oviducts in females open into cloaca.
Detailed Solution for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 5
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 6
Which of the following systems in frog shows presence of both hepatic and renal portal systems?
Detailed Solution for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 6
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 7
What is the function of the nictitating membrane in frogs?
Detailed Solution for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 7
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 8
Which of the following best describes the respiration in frog during hibernation?
Detailed Solution for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 8
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 9
Which of the following glands in frogs are endocrine in nature?
Detailed Solution for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 9
Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 10
Select the correct route for the passage of sperms in male frogs:
Detailed Solution for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - Question 10
Information about Test: Structural Organisation in Animals Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Structural Organisation in Animals, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF