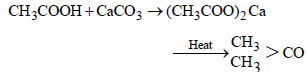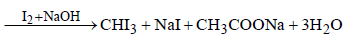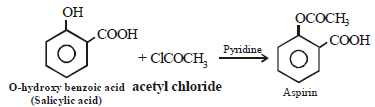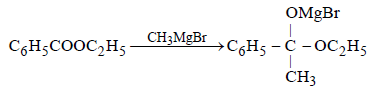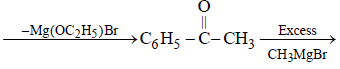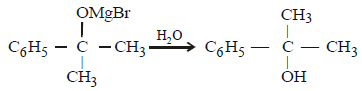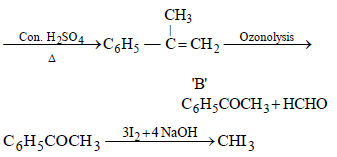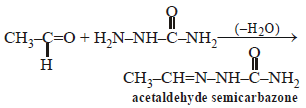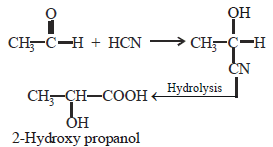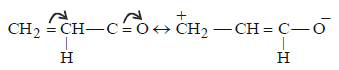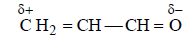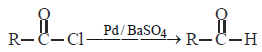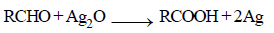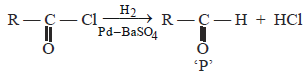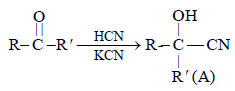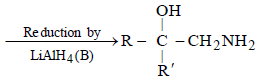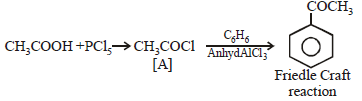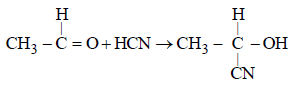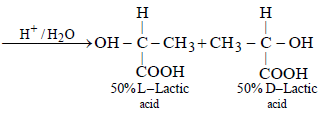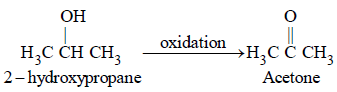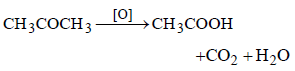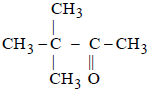31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids - 2
(CH3)3C—CHO does not undergo Aldol condensation due to [1996]
Consider the following transformations :
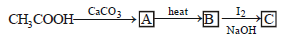
The molecular formula of 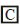 is [1996]
is [1996]
 is [1996]
is [1996]Aspirin is an acetylation product of [1998]
An ester (A) with molecular fomula, C9H10O2 wastreated with excess of CH3MgBr and the complexso formed was treated with H2SO4 to give anolefin (B). Ozonolysis of (B) gave a ketone withmolecular formula C8H8O which shows +veiodoform test. The structure of (A) is [1998]
Which one of the following esters cannotundergo Claisen self-condensation? [1998]
Ketones
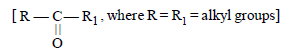 can be obtained in one step by [1998]
can be obtained in one step by [1998]
Iodoform test is not given by [1999]
Acetaldehyde reacts with semicarbazide andforms semicarbazone. Its structure is [1999]
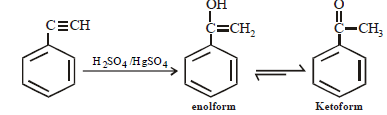
Reaction of phenylacetylene with dil. H2SO4 and HgSO4 gives [1999]
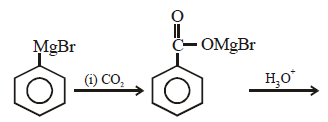
The cyanohydrin of a compound on hydrolysisgives an optically active α-hydroxy acid. Thecompound is [1999]
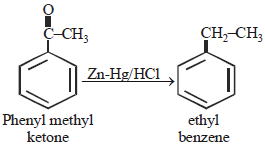
Phenylmethyl ketone can be converted intoethylbezene in one step by which of the followingreagents? [1999]
Polarization of electrons in acrolein may be written as: [2000]
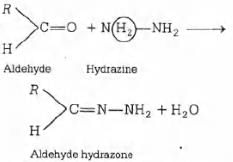
During reduction of aldehydes with hydrazine and potassium hydroxide, the first is the formation
of : [2000]
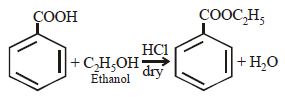
Benzoic acid may be converted to ethyl benzoateby reaction with : [2000]
The catalyst used in Rosenmund's reduction is [2000]
Which of the following is correct? [2001]
Which of the following is incorrect? [2001]
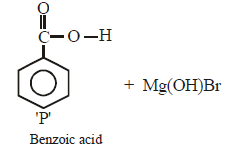
In the following reaction, product 'P' is [2002]
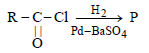
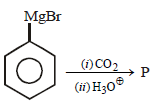
In the above reaction product 'P' is [2002]
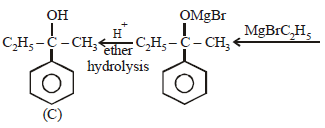
A and B in the following reactions are [2003]
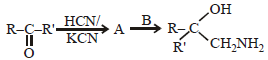
In a set of the given reactions, acetic acid yielded a product C.
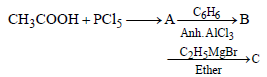
Product C would be - [2003]
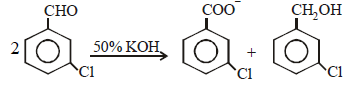
When m-chlorobenzaldehyde is treated with 50% KOH solution, the product(s) obtained is (are) [2003]
In the reaction
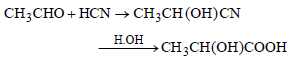
an asymmetric centre is generated. The acid obtained would be [2003]
Which one of the following can be oxidised tothe corresponding carbonyl compound? [2004]
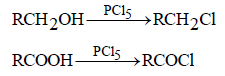
The OH group of an alcohol or the –COOH groupof a carboxylic acid can be replaced by–Cl using [2004]
Formalin is an aqueous solution of [1988]
The reagent (s) which can be used to distinguishacetophenone from benzophenone is (are) [1990]
Acetaldehyde reacts with [1991]
In which of the following, the number of carbonatoms does not remain same when carboxylic acidis obtained by oxidation [1992]
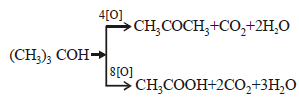
Pinacolone is [1994]
|
9 docs|806 tests
|