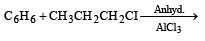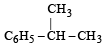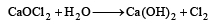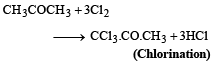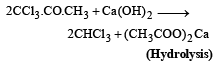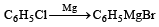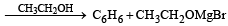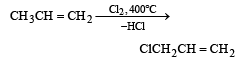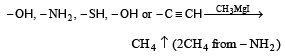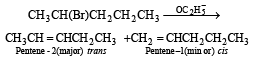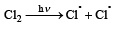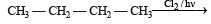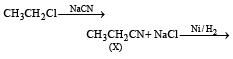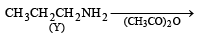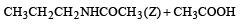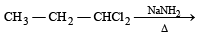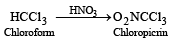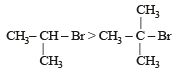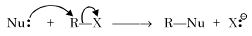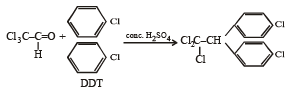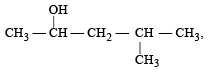31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Haloalkanes & Haloarenes - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Haloalkanes & Haloarenes
Phosgene is a common name for [1988]
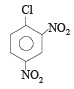
Which chloro derivative of benzene among the following would undergo hydrolysis most readily with aqueous sodium hydroxide to furnish the corresponding hydroxy derivative?
Benzene reacts with n-propyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 to give [1993]
Industrial preparation of chloroform employs acetone and [1993]
Chlorobenzene reacts with Mg in dry ether to give a compound (A) which further reacts with ethanol to yield [1993]
When chlorine is passed through propene at 400°C, which of the following is formed ?[1993]
Zerevitinov’s determination of active hydrogen in a compound is based upon its reaction with[1994]
The replacement of chlorine of chlorobenzene to give phenol requires drastic conditions, but the chlorine of 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene is readily replaced since, [1997]
2-Bromopentane is heated with potassium ethoxide in ethanol. The major product obtained is[1998]
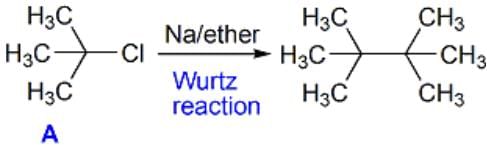
An organic compound A (C4H9Cl) on reaction with Na/diethyl ether gives a hydrocarbon which on monochlorination gives only one chloro derivative, then A is [2001]
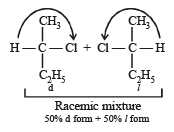
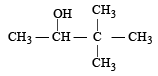
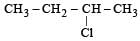 obtained by chlorination of n-butane, will be [2001]
obtained by chlorination of n-butane, will be [2001]
Reactivity order of halides for dehydrohalogenation is [2002]
Z in the above reaction sequence is [2002]
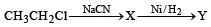

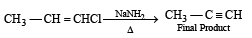
When CH3CH2CHCl2 is treated with NaNH2, the product formed is [2002]
Which of the following is responsible for depletion of the ozone layer in the upper strata of the atmosphere? [2004]
Chloropicrin is obtained by the reaction of
In a SN2 substitution reaction of the type 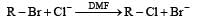 [2008] which one of the following has the highest relative rate ?
[2008] which one of the following has the highest relative rate ?
Which of the following reactions is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction? [2009]
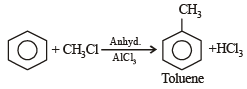
Benzene reacts with CH3Cl in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 to form: [2009]
Trichloroacetaldehyde, CCl3CHO reacts with chlorobenzene in presence of sulphuric acid and produces: [2009]
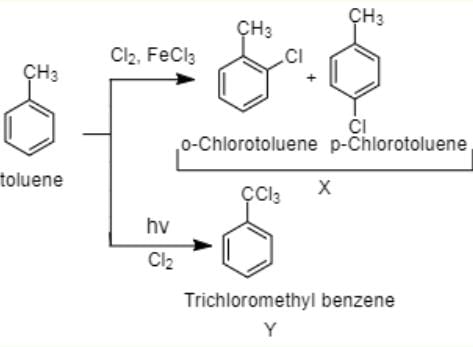
The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in presence of FeCl3 gives ' X' and reaction in presence of light gives ‘Y’. Thus, ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are : [2010]
Which one is most reactive towards SN1 reaction ?
Consider the reactions : [2011 M]
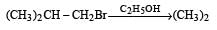
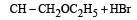
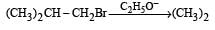
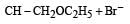
The mechanisms of reactions (i) and (ii) are respectively :
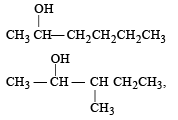
Number of isomeric alcohols of molecular formula C6H14O which give positive iodoform test is [NEET Kar. 2013]
Which of the following is the correct order of boiling points for the given compounds?