Test: CNS ( Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: CNS ( Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain)
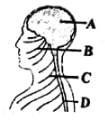
In the accompanying diagram of a part of the human body, the structures belonging to the central neural system are labelled as

All sensory information to be registered consciously by the forebrain must pass via the
Which of the following is a part of our brain?
The correct sequence of meninges from inner to outer side is
Which of these is not a part of the hindbrain?
Direction:
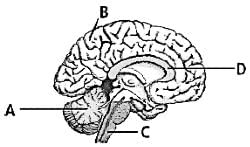
Which labelled part controls the process of breathing?
Direction:
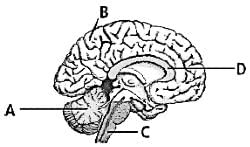
Which of the following functions is performed by the labelled 'C' in the given figure?
Voluntary activities of body are controlled by :-
Which of the following contains cardiovascular reflexes, gastric secretions and the centres that control respiration?
Which part of the brain regulates the body temperature, hunger and water balance :-
Most of the involuntary action are controlled by :-
The membrane which cover the brain and the spinal cord is :-
The box like bony structure which encloses the brain is called :-
Which of these is not a part of the forebrain?
Which part of the neuron is present in a high concentration in the grey matter?
Which of the following is a richly vascular layer with lots of blood capillaries :-
Which of these is not true about the hypothalamus?
If the corpus callosum is removed in mammalian brain then what will be affected :-
Which of these structures are found in the midbrain?



















