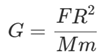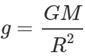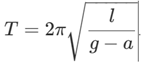Assertion & Reason Test: Gravitation - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Assertion & Reason Test: Gravitation
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: Smaller the orbit of the planet around the sun, shorter is the time it takes to complete one revolution.
Reason: According to Kepler’s third law of planetary motion, square of time period is proportional to cube of mean distance from sun.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: Gravitational force between two particles is negligibly small compared to the electrical force.
Reason: The electrical force is experienced by charged particles only.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: The universal gravitational constant is same as acceleration due to gravity. Reason: Gravitational constant and acceleration due to gravity have same dimensional formula.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: If a pendulum is suspended in a lift and lift is falling freely, then its time period becomes infinite.
Reason: Free falling body has acceleration equal to acceleration due to gravity.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: If earth suddenly stops rotating about its axis, then the value of acceleration due to gravity will become the same at all the places.
Reason: The value of acceleration due to gravity is independent of rotation of earth.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: There is no effect of rotation of earth on acceleration due to gravity at poles.
Reason: Rotation of earth is about the polar axis.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: A force act upon the earth revolving in a circular orbit about the sun. Hence work should be done on the earth.
Reason: The necessary centripetal force for circular motion of earth comes from the gravitational force between earth and sun.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: The ratio of inertial mass to gravitational mass is equal to one.
Reason: The inertial mass and gravitational mass of a body are equivalent.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: Gravitational potential of earth at every place on it is negative.
Reason: Everybody on earth is bound by the attraction of earth.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: A planet moves faster, when it is closer to the sun in its orbit and vice versa.
Reason: Orbital velocity in orbital of planet is constant.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: If an earth satellite moves to a lower orbit, there is some dissipation of energy but the satellite speed increases.
Reason: The speed of satellite is a constant quantity.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: Earth has an atmosphere but the moon does not.
Reason: Moon is very small in comparison to earth.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: Two different planets have same escape velocity.
Reason: Value of escape velocity is a universal constant.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: Generally the path of a projectile from the earth is parabolic but it is elliptical for projectiles going to a very large height.
Reason: The path of a projectile is independent of the gravitational force of earth.
Read the assertion and reason carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
Assertion: Space rockets are usually launched in the equatorial line from west to east.
Reason: The acceleration due to gravity is minimum at the equator.