Assertion & Reason Test: States of Matter (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
8 Questions MCQ Test NCERT Based Tests for NEET - Assertion & Reason Test: States of Matter (Old NCERT)
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): Three states of matter are the result of balance between intermolecular forces and thermal energy of the molecules.
Reason (R): Intermolecular forces tend to keep the molecules together but thermal energy of molecules tends to keep them apart.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): The temperature at which vapour pressure of a liquid is equal to the external pressure is called boiling temperature.
Reason (R): At high altitude, atmospheric pressure is high.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): At constant temperature, pV vs V plot for real gases is not a straight line.
Reason (R): At high pressure, all gases have Z > 1 but at intermediate pressure most gases have Z < 1.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): Liquids tend to have maximum number of molecules at their surface.
Reason (R): Small liquid drops have spherical shape.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): At critical temperature, liquid passes into gaseous state imperceptibly and continuously.
Reason (R): The density of liquid and gaseous phase is equal to critical temperature.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): Gases do not liquefy above their critical temperature, even on applying high pressure.
Reason (R): Above critical temperature, the molecular speed is high and intermolecular attractions cannot hold the molecules together because they escape because of high speed.
Match the graphs between the following variables with their names:
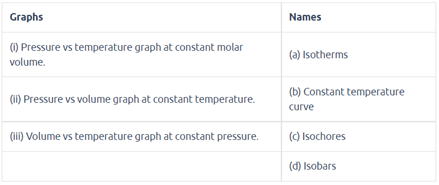
Match the following gas laws with the equation representing them.
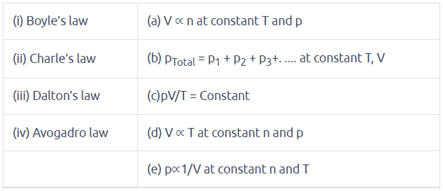
|
748 tests
|




















