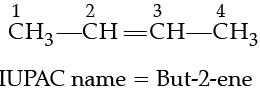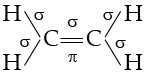Case Based Questions Test: Hydrocarbons - NEET MCQ
8 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: Hydrocarbons
For nomenclature of alkenes in the IUPAC system, the longest chain of carbon atoms containing the double bond is selected. Numbering of the chain is done from the end which is nearer to the double bond. The suffix ‘ene’ replaces ‘ane’ of alkanes. The first member of the alkene series is: CH2 (replacing n by 1 in CnH2n) known as methene but has a very short life. The first stable member of the alkene series is C2H4 known as ethylene (common) or ethene (IUPAC).
Q. The IUPAC name of CH3—CH=CH—CH3 is:
For nomenclature of alkenes in the IUPAC system, the longest chain of carbon atoms containing the double bond is selected. Numbering of the chain is done from the end which is nearer to the double bond. The suffix ‘ene’ replaces ‘ane’ of alkanes. The first member of the alkene series is: CH2 (replacing n by 1 in CnH2n) known as methene but has a very short life. The first stable member of the alkene series is C2H4 known as ethylene (common) or ethene (IUPAC).
Q. The number of σ and π-bonds in C2H4 is ............... and ............. respectively.
For nomenclature of alkenes in the IUPAC system, the longest chain of carbon atoms containing the double bond is selected. Numbering of the chain is done from the end which is nearer to the double bond. The suffix ‘ene’ replaces ‘ane’ of alkanes. The first member of the alkene series is: CH2 (replacing n by 1 in CnH2n) known as methene but has a very short life. The first stable member of the alkene series is C2H4 known as ethylene (common) or ethene (IUPAC).
Q. The correct statement/s for nomenclature of alkenes in the IUPAC system is/are:
For nomenclature of alkenes in the IUPAC system, the longest chain of carbon atoms containing the double bond is selected. Numbering of the chain is done from the end which is nearer to the double bond. The suffix ‘ene’ replaces ‘ane’ of alkanes. The first member of the alkene series is: CH2 (replacing n by 1 in CnH2n) known as methene but has a very short life. The first stable member of the alkene series is C2H4 known as ethylene (common) or ethene (IUPAC).
Q. The general formula of alkenes is:
Alkanes are almost non-polar molecules because of the covalent nature of C—C and C—H bonds and due to very little difference of electronegativity between carbon and hydrogen atoms. They possess weak Van Der Waals forces. Due to the weak forces, the first four members C1 to C4 are gases, C5 to C17 are liquids and those containing 18 carbon atoms or more are solids at 298K. They are colourless and odourless. In alkanes, there is a steady increase in boiling point with the increase in molecular mass. This is due to the fact that the intermolecular Van Der Waals forces increase with increase of the molecular size or the surface area of the molecule. With the increase in branching, the boiling point of alkanes decreases. The given questions (i) to (iv) consist of an assertion (A) and reason (R) statement. Choose the appropriate answer.
Assertion: Alkanes are polar molecules.
Reason: C—C and C—H bonds in alkanes are covalent in nature.
Alkanes are almost non-polar molecules because of the covalent nature of C—C and C—H bonds and due to very little difference of electronegativity between carbon and hydrogen atoms. They possess weak Van Der Waals forces. Due to the weak forces, the first four members C1 to C4 are gases, C5 to C17 are liquids and those containing 18 carbon atoms or more are solids at 298K. They are colourless and odourless. In alkanes, there is a steady increase in boiling point with the increase in molecular mass. This is due to the fact that the intermolecular Van Der Waals forces increase with increase of the molecular size or the surface area of the molecule. With the increase in branching, the boiling point of alkanes decreases. The given questions (i) to (iv) consist of an assertion (A) and reason (R) statement. Choose the appropriate answer.
Assertion: The boiling point of pentane is higher than butane.
Reason: The molecules of pentane possess lesser Van Der Waals forces than butane.
Alkanes are almost non-polar molecules because of the covalent nature of C—C and C—H bonds and due to very little difference of electronegativity between carbon and hydrogen atoms. They possess weak Van Der Waals forces. Due to the weak forces, the first four members C1 to C4 are gases, C5 to C17 are liquids and those containing 18 carbon atoms or more are solids at 298K. They are colourless and odourless. In alkanes, there is a steady increase in boiling point with the increase in molecular mass. This is due to the fact that the intermolecular Van Der Waals forces increase with increase of the molecular size or the surface area of the molecule. With the increase in branching, the boiling point of alkanes decreases. The given questions (i) to (iv) consist of an assertion (A) and reason (R) statement. Choose the appropriate answer.
Assertion: Alkanes are hydrophobic in nature.
Reason: Alkanes are nonpolar molecules.
Alkanes are almost non-polar molecules because of the covalent nature of C—C and C—H bonds and due to very little difference of electronegativity between carbon and hydrogen atoms. They possess weak Van Der Waals forces. Due to the weak forces, the first four members C1 to C4 are gases, C5 to C17 are liquids and those containing 18 carbon atoms or more are solids at 298K. They are colourless and odourless. In alkanes, there is a steady increase in boiling point with the increase in molecular mass. This is due to the fact that the intermolecular Van Der Waals forces increase with increase of the molecular size or the surface area of the molecule. With the increase in branching, the boiling point of alkanes decreases. The given questions (i) to (iv) consist of an assertion (A) and reason (R) statement. Choose the appropriate answer.
Assertion: The first four members of alkanes are gases.
Reason: They possess weak Van Der Waals forces.