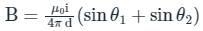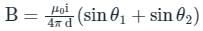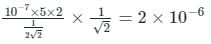Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): Magnetic Field - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): Magnetic Field
How can a magnetic field be produced?
Which one of the Maxwell’s laws leads to the conclusion that there are no magnetic field loops that are not closed?
Which combination of magnetic field lines and poles shows two magnets repelling each other?
Magnetic field strength due to a short bar magnet on its axial line at a distance x is B. What is its value at the same distance on the equatorial line?
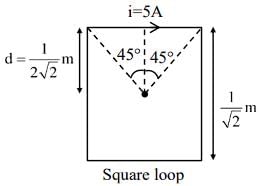
A current of 5A exists in a square loop of side 1√2m. Then the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the square loop will be p × 10–6 T. where, value of p is ______.
[Take µ0 = 4π × 10–7 T mA–1].
When the switch is closed a magnetic field is produced by the coil. Which option shows the shape of the field?
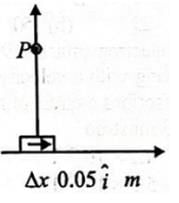
An element of 0.05 m is placed at the origin as shown in figure which carries a large current of 10A. distance of 1m in perpendicular direction. The value of magnetic field is
A rectangular coil of 400 turns and 10−2m2 area, carrying a current of 0.5 A, is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 1 T such that the plane of the coil makes an angle of 60∘ with the direction of the magnetic field. The initial moment of force acting on the coil in Nm is
A compass has a small balanced pointer that always points North-South. This is because:
A current I flows along the length of an infinitely long, straight, thin walled pipe. Then