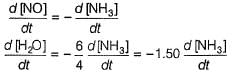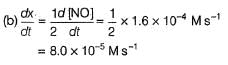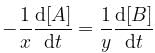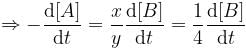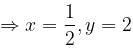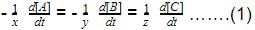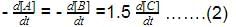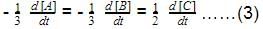Rate Law, Molecularity & Order of a Chemical Reaction - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Rate Law, Molecularity & Order of a Chemical Reaction
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?
4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O
4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O
The rate of formation of NO(g) in the reaction, 2NOBr(g) → 2NO(g) + Br2(g) was reported as 1.6 x 10-4 Ms-1. Thus, rate of the reaction is
Rate of formation of SO3 in the reaction below is 100 kg min-1.
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
Hence, rate of disappearance of SO2 will be:
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
Hence, rate of disappearance of SO2 will be:
The following reaction can take place in both directions:
For the forward reaction, the rate varies with the concentration of A as and for the backward reaction,
Hence, net reaction rate is:
For a reaction, xA → yB, rate of disappearance of ‘A’ is related to the rate of appearance of 'B' by the equation
Thus, x and y respectively are
For the reaction,
H2(g) + A2(g) 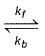 2H(g) + A2(g)
2H(g) + A2(g)
kf = 2.2 x 104 L mol-1s-1 and Kc = 1.00 x 10-4 at 3000 K. Thus, kb is
For a reaction,
hen x, y and z are
For the reaction,
2N2O5(g) → 4NO2 (g) + O2(G)
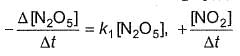
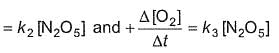
Thus,
The decomposition of acetaldehyde is given by the following reaction:
CH3CHO(g) → CH4(g) + CO(g)
Rate of the reaction with respect to the pressure of the reactant is
For the reaction,
then rate law is
For gaseous reaction, the rate can be expressed as
The initial rates of reaction for the equation, 2A + B → Products.
Products were determined under various initial concentrations of reactants.
Thus, rate law is equal to
For the reaction, A + 2B → Product, the reaction rate was halved on doubling the concentration of A. Thus, order w.r.t. A is
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 and 15) This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-1
2 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).
Q. What is the rate law when observed rate is 1.35 x 10-5 mol L-1 s-1 at [NO2] = 0.005 mol L-1?
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-1
2 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).
Q. Rate constant of the reaction will be
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-18) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
In the following reaction
Q. Where negative sign indicates rate of disappearance of the reactant. What is the value of x/y ?
The reaction rate is defined as the rate at which the concentration of the reactants __________ with time or the concentration of products ___________ with time.
In a certain polluted atmosphere containing O3 at a steady concentration of 2.0 x 10-6 M, the hourly production of O3 by all sources was estimated as 7.2 x 10-15 M. If the only mechanism for destruction of O3 in the second-order reaction is
2O3 → 3O2
then rate constant for destruction reaction, defined by the rate law for - Δ[O3]/Δf is x * 10-7 M-1 s-1 . What is the value of x?
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
For a reversible reaction, net rate is
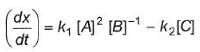
hence given reaction is
Reaction kinetics deals with the study of
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|