Test: Alkene Oxidation Reaction - NEET MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Alkene Oxidation Reaction
Direction (Q, Nos. 1 - 5) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Which molecule will give the following dicarboxylic acid upon treatment with acidic solution of KMnO4?
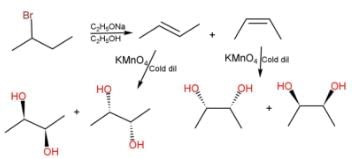
An optically active alky bromide X (C6H13Br) upon treatment with ethanolic KOH solution forms two alkenes Y and Z with their molecular formula (C6H12). Y and Z are positional isomers. Z upon treatment with cold, dilute alkaline KMnO4 solution gives a meso-diol. Hence, X is
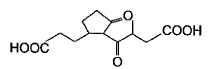
Which starting material should be used to produce the compound shown below?
When reacted with an alkene, which of the following reagent would not introduce I atleast one hydroxyl (— OH) group into final product?
Direction (Q. Nos. 6 - 9) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
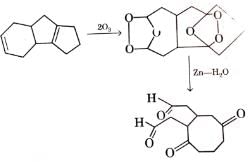
Q. Which of the following compound(s) on reductive ozonolysis (O3/ Zn - H2O) would produce octane-2, 4, 5, 7-tetraone?
A hydrocarbon X (C10H16) upon catalytic hydrogenation gives 4-methyl-1 -isopropyl cyclohexane. Also, X upon ozonation followed by hydrolysis in the presence of Zn gives CH2O and
The correct statement(s) concerning X is/are
A compound X (C5HgBr) is optically active. X on treatment with KOH in ethanol gives Y (C5H8) as major product. Ozonolysis of Y followed by Zn-hydrolysis gives Z (C5H8O2) . Z forms yellow precipitate with NaO H/l2 as well as it reduces Tollen’s reagent. Z on treatment with Zn (Hg)/HCI gives pentane. The correct statement(s) regarding X, Y and Z is/are
Consider the following reaction sequence.
The correct statement(s) regarding diois formed in the final step is/are
Direction (Q. Nos. 10-14) This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Six questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
An unknown compound X (C5HgBr) does not decolourise purple colour of alkaline permanganate solution. Upon treatment with C2H5OK/C2H5OH, X gives Y (C5H8) as only structural isomer. Catalytic hydrogenation of Y gives methyl cyclobutane. Ozonolysis of Y gives Z (C5H8O2) which can exist as a pair of enantiomers.
Q. The correct statement concerning X is
Passage I
An unknown compound X (C5HgBr) does not decolourise purple colour of alkaline permanganate solution. Upon treatment with C2H5OK/C2H5OH, X gives Y (C5H8) as only structural isomer. Catalytic hydrogenation of Y gives methyl cyclobutane. Ozonolysis of Y gives Z (C5H8O2) which can exist as a pair of enantiomers.
Q.
What is true regarding reaction of Y with cold, dilute alkaline KMnO4 solution?
Passage I
An unknown compound X (C5HgBr) does not decolourise purple colour of alkaline permanganate solution. Upon treatment with C2H5OK/C2H5OH, X gives Y (C5H8) as only structural isomer. Catalytic hydrogenation of Y gives methyl cyclobutane. Ozonolysis of Y gives Z (C5H8O2) which can exist as a pair of enantiomers.
Q. What is correct skeleton of Z?
Passage II
An organic compound X (C7H11Br) shows optical isomerism as well as decolourises brown colour of bromine water solution. X on treatment with HBr in the absence of a peroxide forms a pair of diastereomers, both of them are optically active. Also, X with C2H5ONa in C2H5OH gives a single product Y (C7H10). Y on treatment with ozone followed by reduction with (CH3)2S gives 1, 3,-cyclopentanedione as one product.
Q. The structure of compound X is
Passage II
An organic compound X (C7H11Br) shows optical isomerism as well as decolourises brown colour of bromine water solution. X on treatment with HBr in the absence of a peroxide forms a pair of diastereomers, both of them are optically active. Also, X with C2H5ONa in C2H5OH gives a single product Y (C7H10). Y on treatment with ozone followed by reduction with (CH3)2S gives 1, 3,-cyclopentanedione as one product.
Q. The correct statement regarding produces) formed by the reaction of X with HBr in th e presence of H2O2 is
Passage II
An organic compound X (C7H11Br) shows optical isomerism as well as decolourises brown colour of bromine water solution. X on treatment with HBr in the absence of a peroxide forms a pair of diastereomers, both of them are optically active. Also, X with C2H5ONa in C2H5OH gives a single product Y (C7H10). Y on treatment with ozone followed by reduction with (CH3)2S gives 1, 3,-cyclopentanedione as one product.
Q. The correct statement concerning product(s) formed when Y is treated with excess of HCI is
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 19) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
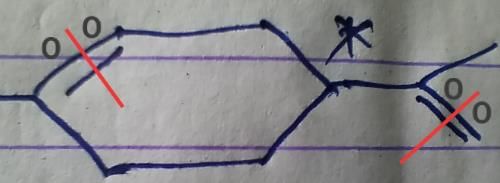
How many different isomers of alkene (X)can give the above reaction?
If all stereoisomers of 2-pentene are treated with cold, dilute and alkaline KMn04 solution, how many different diols would be expected?
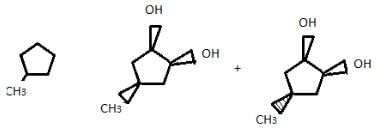
If 4-methyl cyclopentene is treated with OsO4 followed by work-up with NaHSO3/H2O, how many different diols would result?
A mixture containing all the stereoisomers of 3, 4, 5-trimethyl cyclopentene is treated with O3 followed by Zn-hydrolysis, how many different isomers of products would result?
Direction (Q. Nos. 20 and 21) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Statement I : In reductive ozonolysis, dimethylsulphide is better reducing reagent than Zn- H2O.
Statement II : (CH3)2S brings about homogeneous catalysis.
Statement I : cis-2-butene with cold, dilute, alkaline KMnO4 gives meso-2,3- butanediol.
Statement II : In alkaline solution, under cold condition, KMnO4 acts as a mild oxidising agent.