Test: Biodiversity (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Biodiversity (NCERT)
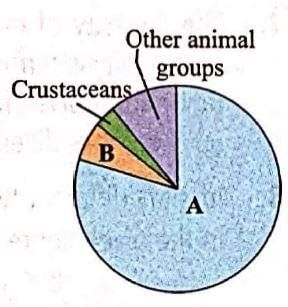
Given pie diagram represents the proportionate number of species of major groups of invertebrates. Identify the groups A and B.

Dodo, passenger pigeon and Steller's sea cow become extinct in the last 500 years due to
Species diversity______as we move away from the _______towards_____.
On a logarithmic scale, the species area relationship is a straight line described by the equation log S = log C + Z log A.
What does S, C, Z and A represent in the given equation? Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Species richness = 1
Slope of the line = 2
Y- intercept = 3
Area = 4
There are four major causes of accelerated rates of species extinction, which are collectively called as 'the evil quartet'. Which one of the following is not included in 'the evil quartet'?
An exotic species that is introduced to a new area, spreads rapidly and eliminates native species is called
The exotic species, which when introduced in India became notorious weed(s), is/are
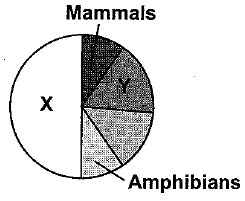
The given pie diagram represents the proportionate number of species of major taxa of vertebrates. Identify the group A and B.
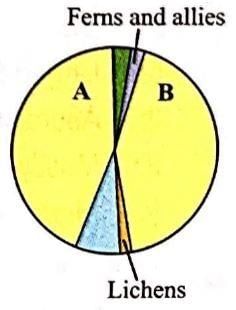
Identify the groups of organism marked A and B in the given pie diagram representing the proportionate number of species of major taxa of plants.
Which of the following fish led to the extinction of an ecologically unique assemblage of more than 200 species of cichlid fish in the take Victoria of E. Africa?
Which one of the following fish is being illegally introduced for aquaculture purposes and is posing a threat to the indigenous catfishes of Indian rivers?
When a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated with it in an obligatory way also become extinct. This phenomenon is referred to as
Character of a stable community is that it
(a) should not show too much variations in year-to-year productivity
(b) must be resistant to occasional natural or man-made disturbances
(c) should be resistant to invasions by alien species
(d) all of these
Which of the following statements describe natural extinction?
(i) Extinctions abetted by human activities
(ii) Slow replacement of existing species
(iii) Also known as background extinction
(iv) A small population is most likely to be extinct
Which of the following statements regarding the estimates of number of species found on earth is not correct?
What is the decreasing order of the number of animals species as far as India is concerned?
How many plant and animal species have been discovered and described so far?
Species diversity______as one moves from high to low altitudes.
What is the total number of species present on earth as estimated by Robert May?
India is one of the 12 megadiversity countries of the world and is being divided into______biogeographical regions.
What is the global species diversity according to Robert May?
Of all the plant species recorded which class has the minimum number of species?
Read the given statement and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Tropical rainforests are disappearing fastly from developing countries such as India.
Statement 2: No value is attached to these forests because these are poor in biodiversity
Oragnisation responsible for maintaining Red Data Book is
Amazon rainforests are considered as 'lungs of the planet' as they contribute______of the total oxygen in the earth's atmosphere.
Introduction of alien species into new area poses a threat to extinction of indigenous species due to
Genetic variations affect the production of the drug reserpine in the medicinal plant Rauwolfia vomitoria growing in different Himalayan ranges. What kind of diversity does it indicate?
Western ghats have a greater number of amphibian species than the Eastern ghats. What kind of diversity does it represent?
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.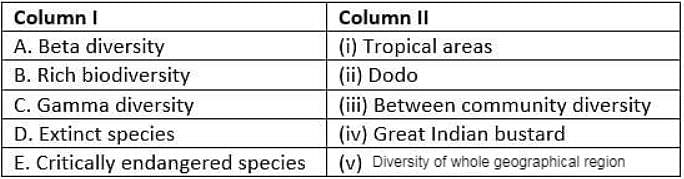
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|




















