Test: Bond Dissociation Enthalpy - JEE MCQ
18 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Bond Dissociation Enthalpy
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains 13 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
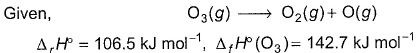
Q. Thus, (BE) of 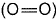 bond in O2 is
bond in O2 is
ΔfH° of CS2 = 117.36 kJ mol-1
C(g) = 716.682 kJ mol-1
S(g) = 278.805 kJ mol-1
Q. Thus,  bond enthalpy in CS2 is
bond enthalpy in CS2 is
S(g) = 278.805 kJ mol-1
The dissociation energy of CH4 and C2H6 to convert them into gaseous atoms are 360 and 620 kcal mol-1 respectively. Thus, bond energy of (C—C) bond is
The (C— Cl) bond energy of CCI4 (l) can be derived from thermochemical data
Bond dissociation energy of = + 590 kJ mol-1 and that of (C—C) = + 331 kJ mol-1 at 298 K.
Enthalpy change for the polymerisation of ethene to polyethene is (where n is large integral value)
Given at 298 K
Q. The resonance energy of benzene is
Given the following thermochemical data at 298 K and 1 bar
ΔH°vap (CH3OH) = 38.0 kJ mol-1
ΔfH°: H(g) = 218 kJ mol-1
O(g) = 249 kJ mol-1
C(g) = 715 kJ mol-1
Bond dissociation energy
(C—H) = 415 kJ mol-1
(C—O) = 356 kJ mol-1
(O—H) = 4 6 3 kJ mol-1
Q. The ΔfH° of liquid methyl alcohol in kJ mol-1 is
Heat of hydrogenation of ethene is x1 and that of benzene is x2. The resonance energy of benzene is
Given, BE of = 498.8 kJ mol-1
BE of (O—O) in ozone = 302.3 kJ mol-1
Q. What is enthalpy change of the reaction
The standard enthalpies of formation of SF6 (g), S (g)and F (g) are -1100, + 275 and + 80 kJ mol-1. Thus, average bond energy of (S—F) in SF6 is
Calculate resonance energy of N2O from the following data
ΔfH° (N2O) = 82 kJ mol-1
Given, ΔfH° (H2S) = 20.1 kJ mol-1
ΔfH° (H)(g) = +218.0 kJ mol-1
ΔfH° (S) (g) = +277.0 kJ mol-1
and bond dissociation energy of first (H—S) bond in H2S is 376.6 kJ mol-1. Thus, ΔfH° (HS)is
Given, BE (H—H) - x1, BE = x2, BE (O—H) = x3 and for H2O (l) → H2O (g), ΔH = x4 mol-1, then ΔfH° [H2O (l)] is
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 -15) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d).
Based on the following thermochemical data of the given process, answer the questions.
Q. Bond energy of (C— C) bond is
Based on the following thermochemical data of the given process, answer the questions.
Q. Bond energy of (C—H) bond is
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Given bond dissociation energy under standard states.
Q. i. Number of and
bonds in (A) is ......
Given bond dissociation energy under standard states.
Q. ii. Number of and
) bond in (B) is .......
Direction (Q. Nos. 18) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. Given thermochemical data under standard states at 278 K and 1 bar.
Match the types of bonds in Column I with their respective value of bond-energy in Column II and select answer from the codes given below the table














