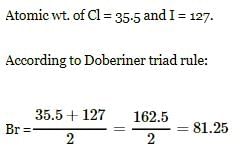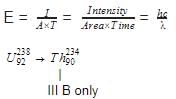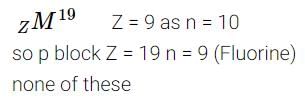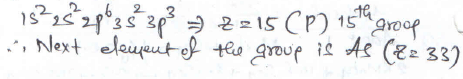Test: Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties - 2 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties - 2
Which of the following is not a Dobereiner triad -
Which of the following set of elements obeyes Newland’s octave rule -
Which of the following will not form crystalline structure with oppositely charged ions
Which is not anomalous pair of elements in the Medeleeves periodic table -
Elements in the same vertical group of the periodic table have same
The places that were left empty by Mendeleev were, for -
Which of the following pairs of elements do not follow octave rule -
Elements which occupied position in the lother meyer curve, on the peaks, were -
Modern periodic table is based on atomic no. experiments which proved importance of at no. was -
Atomic no. is the base of -
(i) Lother meyer curve
(ii) Newland octave rule
(iii) Modern periodic table
(iv) Doeberiener triad rule
(v) Long form of periodic table
Atomic wt. or Cl = 35.5 and of I = 127. According to doeberiner triad rule, At. wt. of Br will be -
The elements of groups, 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16 and 17 are collectively called -
Justification of putting H in VII A group is -
The discovery of which of the following group of elements gave a death blow to the Newlands Law -
Which of the following pair of elements follows Newland’s octave rule -
(IIIB) changes to
by emission of α-particle. Daughter element will be in -
From the list given below, elements which belongs to the same group or sub-group are -
The name ‘Rare earths’ is used for -
Z/e ratio for N3-, O2- and F- respectively will be -
There are 10 neutrons in the nucleus of the element zM19. It belongs to -
Which of the following is not an actinoid?
the electronic configuration of an element is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3. the atomic number of the element which is just below the above element in the periodic table is ________
The number of elements in 5th and 6th period of periodic table are respectively -
Atomic number of Ag is 47. In the same group the atomic number of elements placed above and below Ag will be -
Atomic number 15, 33, 51 represents the following family -
The atom having the valence shell electronic configuration 4s2 4p2 would be in -
The number of elements know at that time when Mendeleev arranged them in the periodic table was-
As applied to periodic table, which of the following sets include only magic numbers -
In the general electronic configuration -
(n - 2)f1-14 (n - 1)d0-1 ns2, if value of n = 7 the configuration will be -
The correct order of atomic size of C, N, P, S follows the order -