Test: Classification of Non-Chordates - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test NCERTs at Fingertips: Textbooks, Tests & Solutions - Test: Classification of Non-Chordates
Which one of the following groups of three animals is- correctly matched with their one chiaracteristic morphological feature?
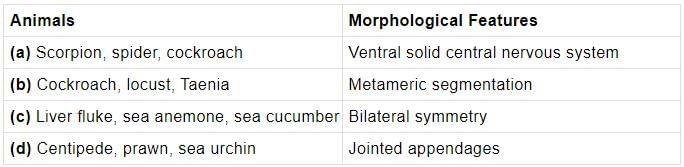

Which one of the following is a matching set of a phylum and its three examples?
What is true about Nereis, scorpion, cockroach and sliver fish?
Bilateral symmetry, metameric segmentation, coelom and open circulatory system chiaracterizes which of the following phylum?
Which one of the following statements about certain given animals is correct?
Which of the following have porous body and are diploblastic?
Phylum Mollusca can be distinguished from other invertebrates by the presence of
Which of the following is not a characteristic feature of sponges?
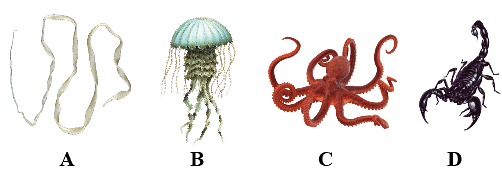
The figures (A - D) show four animals. Select the correct option with respect to a common characteristic of two of these animals.
Which of the following statements are incorrect?
(i) Parapodia are lateral appendages in arthropods used for swimming.
(ii) Radula in molluscs are structures involved in excretion.
(iii) Aschelminthes are dioecious.
(iv) Echinoderm adults show radial symmetry.
(v) Ctenophorans are diploblastic.
In v/hich one of the following, the genus name, its two characters and its phylum are not correctly matched?

Read the following statements and select the incorrect ones.
(i) Circulatory system in arthropods is of closed type.
(ii) Parapodia in annelids help in swimming.
(iii) Phylum Mollusca is the second largest animal phylum after arthropods
(iv) Aschelminthes are dioecious.
What is common between earthworm and Periplaneta?
In which of the following, segmentation in the body is first observed?
Which one of the following features is common in silver fish, scorpion, dragonfly and prawn?
Consider the following statements (A - C) each with two blanks.
A. Animals like Hydra and Jelly fish depict (i) symmetry whereas all vertebrates show (ii) symmetry.
B. In fiii) and (iv) digestive tract has only sngle opening (mouth) and is said to be incomplete.
C. Trichinella (Trichina worm) is a cosmopolitan (v) parasite whereas Fasciola (liver fluke) lives in the ducts of the liver of (vi)
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill ups for the respective blank numbers from (i) to (vi) in the statements?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Blood is colourless in the insects.
Statement 2 : Insect blood has no role in O2 transport.
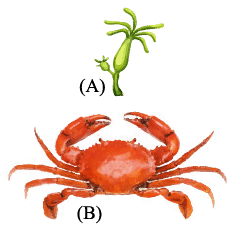
The type of symmetry in the given animals is
Stinging capsules (nematocysts) are found in
Which of the following statements is correct for sponges without exception?
What is common among silver fish, scorpion, crab and honey bee?
Among the following organisms which is a completely non-parasitic form?
Reason (R): These characteristics help molluscs in locomotion and protecting their internal organs.
|
257 docs|234 tests
|




















