Test: Conductance of Electrolytic Solutions - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Conductance of Electrolytic Solutions
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-19) This section contains 19 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
The correct expression in SI system relating the equivalent conductance 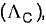 specific conductance (K) and equivalent concentration (C) is (Given k in S cm-1, C in equivalent dm-3)
specific conductance (K) and equivalent concentration (C) is (Given k in S cm-1, C in equivalent dm-3)
Conductivity (K) of 0.01 M NaCI solution is 0.00145 Scm-1. What happens to the conductivity if extra 100 mL of H2O be added to the above solution?
An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to
Specific conductance of 0.01 N KCI solution is x Scm-1 having conductance y S. Thus, specific conductance of 0.01 N NaCI having conductance zS is (in S cm-1)
In terms of (molar conductance),
(molar conductance of very dilute solution) ionisation constant (Ka) of weak acid is
Given limiting ionic conductance of H+ ion : 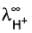 = 350 S cm2 equi-1 and of
= 350 S cm2 equi-1 and of 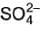 ion :
ion : 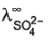 = 80 S cm2 equi-1 Thus for H2SO4, limiting values of molar conductance and equivalent conductance are
= 80 S cm2 equi-1 Thus for H2SO4, limiting values of molar conductance and equivalent conductance are
500 mL of an aqueous solution contains 0.1 mole of KCl. If its specific conductance is x Scm-1, its molar conductance will be (in Scm2 mol-1)
Resistivity of a metal is equal to resistance when cell is constant is
Which quantity is temperature independent?
0.1 M H2SO4 solution is diluted to 0.01 M H2SO4 ?.Hence its molar conductivity will be
Conductivity (Siemen's S) is directly proportional to the area of the vessel and the concentration of the solution in it, and is inversely proportional to the length of the vessel,then constant of proportionality is expressed in
Given, (Scm2 mol-1)for different electrolytes
Thus, of CH3COOH is
Resistance of 0.2 M soluton of an electrolyte is 50?. The specific conductance of solution is 1.3 Sm-1. If resistance of the 0.4 M solution of the same electrolyte is 260Ω, its molar conductivity is
[AlEEE 2011]
The equivalent conductance of NaCl at concentration C and at infinite dilution are λc and λ∞ respectively.The correct relationship λc and λ∞ between is given as (where constanr B is positive).
At 298 K, given specific conductance of saturated
AgCl solution=3.41 x 10-6 Ω-1 cm-1 and that of water used =1.60 x 10-6 Ω-1 cm-1.
Equivalent conductance of saturated AgCl solution= 138.3 Ω-1 cm2 equiv-1
Thus, solubility product (KSp) of AgCl is
AgNO3 (aq) was added to an aq. KCl solution gradually and the conductivity of the solution was measured.the plot of conductance vs the volume of AgNO3 is
[IIT JEE 2011]
Resistance of 0.2 M solution of an electrolyte is 50Ω.The specific conductance of this solution is 1.4 Sm-1. The resistance 0.5 M solution of the same electrolyte is 280Ω. The molar conductivity of 0.5 solution of the electrolyte in Sm2mol-1 is
[JEE Main 2014]
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Equivalent conductance of 0.01 N CaCl2 solution is 126.36 S cm2 equiv-1. This is equal to
Degree of dissociation of very pure water is 1.9 x 10-9. Also limiting molar conductance of λ0(H+) = 350 Scm2 equiv-1 , λ0(OH+) = 200 Scm2 equiv-1
Thus,equivalent conductance of water is
Matching List Type
Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct
Q.
An aqueous solution of X is added slowly to an aqueous solution of Y as Shown in column I.The variation in conductivity of these reactions is given in Column II.Match Column I with Column II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists.
Limiting equivalent conductance (in S cm2 equiv-1) of a weak monobasic acid (HA) at infinite dilution is 100 and that of its 0.01 M solution is 5 at 298K.Match the parameters given in Column I with their values in Column II and select the answer from the codes given.
Comprehension Type
Direction : This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Four questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
Consider the following solutions of an electrolyte
Q.
Conductivity.of 0.2 M solution is
Passage I
Consider the following solutions of an electrolyte
Q.
Molar conductivity of 0.2 M solution is
Passage II
Given molar conductance of 0.001 M NH4OH solution at 298K = 3.0 x 10-3Sm2mol-1.
Limiting molar conductance of
aq. NH4CI = 1.50 x 10-2Sm2mol-1
aq. NaCl = 1.26 x 10-2Sm2 mol-1
and aq. NaOH = 2.48 x 10-2 Sm2 mol-1
Q.
Degree of dissociation of NH4OH at 298 K is
Passage II
Given molar conductance of 0.001 M NH4OH solution at 298K = 3.0 x 10-3Sm2mol-1.
Limiting molar conductance of
aq. NH4CI = 1.50 x 10-2Sm2mol-1
aq. NaCl = 1.26 x 10-2Sm2 mol-1
and aq. NaOH = 2.48 x 10-2 Sm2 mol-1
Q.
pKb of NH4OH is
One Integer Value Correct Type
This section contains 2 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q.
0.01 M aqueous solution of a dibasic acid is diluted to 0.004N such that equivalent conductance is x times.What is the value of x?
At what serial number reciprocal of resistance is given?
(1) Volt
(2) Ampere
(3) Coulomb
(4) Faraday
(5) Conductivity
(6) Resistivity
(7) Siemen
(8) Debye
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 1 multiple choice question. A question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q.
The equivalent conductance of two strong electrolytes at infinite dilution in H2O
(where ions move freely through a solution) at 25°C are given below:
Q.
What additional information/quantity are needed to calculate of an aqueous solution of acetic acid?




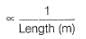
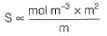
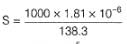
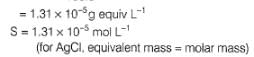
 Ag+ + Cl-
Ag+ + Cl-










